Cache Memory-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Cache Memory.
We have discussed-
- Cache memory is a random access memory.
- It lies on the path between the processor and the main memory.
- It bridges the speed mismatch between the fastest processor and the slower main memory.
Also Read- Cache Mapping Techniques
Cache Lines-
| Cache memory is divided into equal size partitions called as cache lines. |
- While designing a computer’s cache system, the size of cache lines is an important parameter.
- The size of cache line affects a lot of parameters in the caching system.
The following results discuss the effect of changing the cache block (or line) size in a caching system.
Result-01: Effect of Changing Block Size on Spatial Locality-
| The larger the block size, better will be the spatial locality. |
Explanation-
Keeping the cache size constant, we have-
Case-01: Decreasing the Block Size-
- A smaller block size will contain a smaller number of near by addresses in it.
- Thus, only smaller number of near by addresses will be brought into the cache.
- This increases the chances of cache miss which reduces the exploitation of spatial locality.
- Thus, smaller is the block size, inferior is the spatial locality.
Case-02: Increasing the Block Size-
- A larger block size will contain a larger number of near by addresses in it.
- Thus, larger number of near by addresses will be brought into the cache.
- This increases the chances of cache hit which increases the exploitation of spatial locality.
- Thus, larger is the block size, better is the spatial locality.
Result-02: Effect of Changing Block Size On Cache Tag in Direct Mapped Cache-
| In direct mapped cache, block size does not affect the cache tag anyhow. |
Explanation-
Keeping the cache size constant, we have-
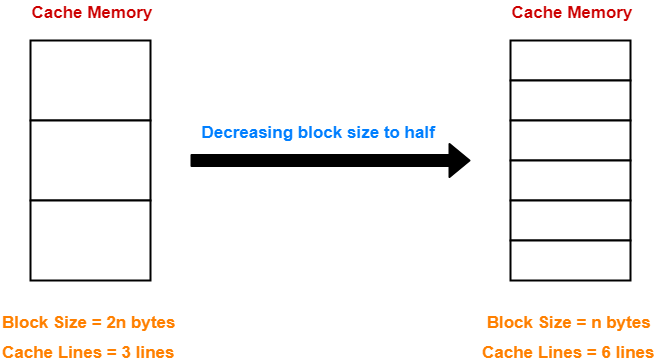
Case-01: Decreasing the Block Size-
- Decreasing the block size increases the number of lines in cache.
- With the decrease in block size, the number of bits in block offset decreases.
- However, with the increase in the number of cache lines, number of bits in line number increases.
- So, number of bits in line number + number of bits in block offset = remains constant.
- Thus, there is no effect on the cache tag.
Example-
Case-02: Increasing the Block Size-
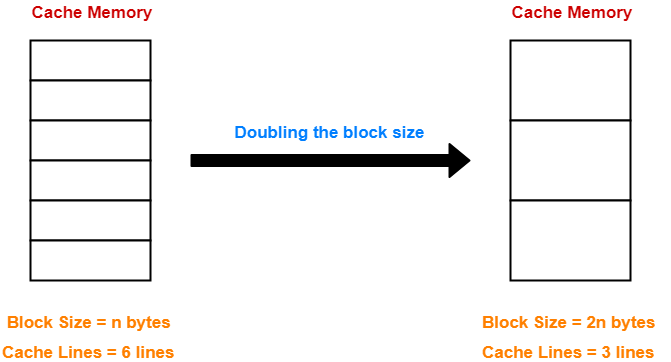
- Increasing the block size decreases the number of lines in cache.
- With the increase in block size, the number of bits in block offset increases.
- However, with the decrease in the number of cache lines, number of bits in line number decreases.
- Thus, number of bits in line number + number of bits in block offset = remains constant.
- Thus, there is no effect on the cache tag.
Example-
Result-03: Effect of Changing Block Size On Cache Tag in Fully Associative Cache-
| In fully associative cache, on decreasing block size, cache tag is reduced and vice versa. |
Explanation-
Keeping the cache size constant, we have-
Case-01: Decreasing the Block Size-
- Decreasing the block size decreases the number of bits in block offset.
- With the decrease in number of bits in block offset, number of bits in tag increases.
Case-02: Increasing the Block Size-
- Increasing the block size increases the number of bits in block offset.
- With the increase in number of bits in block offset, number of bits in tag decreases.
Result-04: Effect of Changing Block Size On Cache Tag in Set Associative Cache-
| In set associative cache, block size does not affect cache tag anyhow. |
Explanation-
Keeping the cache size constant, we have-
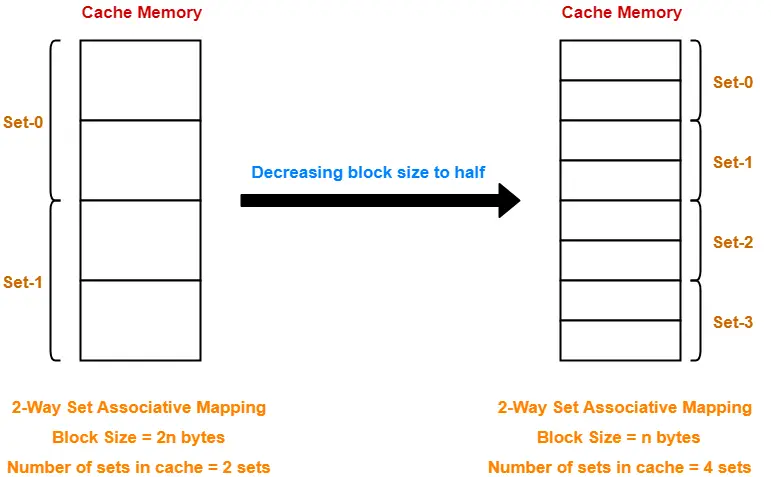
Case-01: Decreasing the Block Size-
- Decreasing the block size increases the number of lines in cache.
- With the decrease in block size, number of bits in block offset decreases.
- With the increase in the number of cache lines, number of sets in cache increases.
- With the increase in number of sets in cache, number of bits in set number increases.
- So, number of bits in set number + number of bits in block offset = remains constant.
- Thus, there is no effect on the cache tag.
Example-
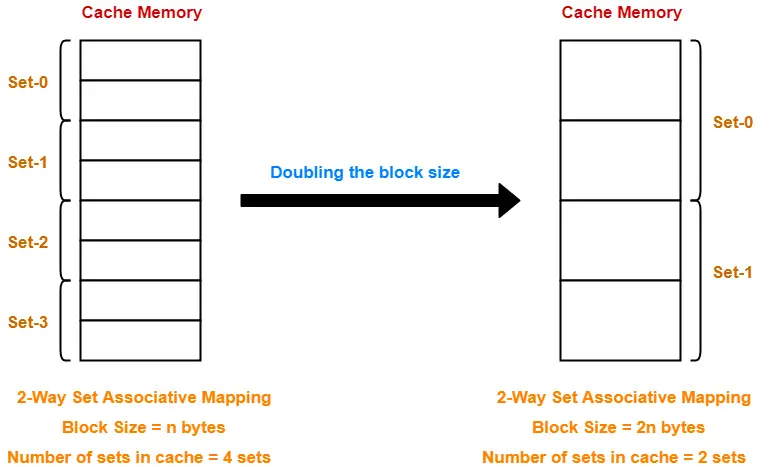
Case-02: Increasing the Block Size-
- Increasing the block size decreases the number of lines in cache.
- With the increase in block size, number of bits in block offset increases.
- With the decrease in the number of cache lines, number of sets in cache decreases.
- With the decrease in number of sets in cache, number of bits in set number decreases.
- So, number of bits in set number + number of bits in block offset = remains constant.
- Thus, there is no effect on the cache tag.
Example-
Result-05: Effect of Changing Block Size On Cache Miss Penalty-
| A smaller cache block incurs a lower cache miss penalty. |
Explanation-
- When a cache miss occurs, block containing the required word has to be brought from the main memory.
- If the block size is small, then time taken to bring the block in the cache will be less.
- Hence, less miss penalty will incur.
- But if the block size is large, then time taken to bring the block in the cache will be more.
- Hence, more miss penalty will incur.
Result-06: Effect of Cache Tag On Cache Hit Time-
| A smaller cache tag ensures a lower cache hit time. |
Explanation-
- Cache hit time is the time required to find out whether the required block is in cache or not.
- It involves comparing the tag of generated address with the tag of cache lines.
- Smaller is the cache tag, lesser will be the time taken to perform the comparisons.
- Hence, smaller cache tag ensures lower cache hit time.
- On the other hand, larger is the cache tag, more will be time taken to perform the comparisons.
- Thus, larger cache tag results in higher cache hit time.
PRACTICE PROBLEM BASED ON CACHE LINE-
Problem-
In designing a computer’s cache system, the cache block or cache line size is an important parameter. Which of the following statements is correct in this context?
- A smaller block size implies better spatial locality
- A smaller block size implies a smaller cache tag and hence lower cache tag overhead
- A smaller block size implies a larger cache tag and hence lower cache hit time
- A smaller bock size incurs a lower cache miss penalty
Solution-
Option (D) is correct. (Result-05)
Reasons-
Option (A) is incorrect because-
- Smaller block does not imply better spatial locality.
- Always, Larger the block size, better is the spatial locality.
Option (B) is incorrect because-
- In direct mapped cache and set associative cache, there is no effect of changing block size on cache tag.
- In fully associative mapped cache, on decreasing block size, cache tag becomes larger.
- Thus, smaller block size does not imply smaller cache tag in any cache organization.
Option (C) is incorrect because-
- “A smaller block size implies a larger cache tag” is true only for fully associative mapped cache.
- Larger cache tag does not imply lower cache hit time rather cache hit time is increased.
Next Article- Magnetic Disk | Important Formulas
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Organization and Architecture.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.