IP Address in Networking-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on IP Address.
We have discussed-
- IP Address is a unique address assigned to each computing device in an IP network.
- ISP assigns IP Address to all the devices present on its network.
- Casting refers to transmitting data (stream of packets) over the network.
Also Read- Types of Casting
In this article, we will discuss some practice problems based on IP Address.
Important Points-
Point-01:
For any given IP Address,
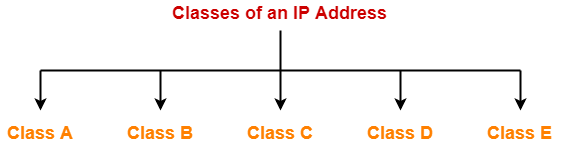
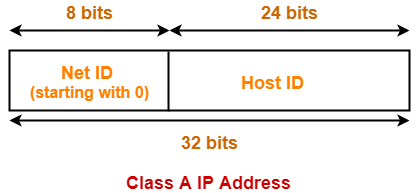
- If the range of first octet is [1, 126], then IP Address belongs to class A.
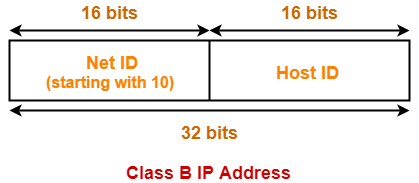
- If the range of first octet is [128, 191], then IP Address belongs to class B.
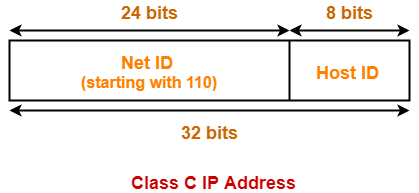
- If the range of first octet is [192, 223], then IP Address belongs to class C.
- If the range of first octet is [224, 239], then IP Address belongs to class D.
- If the range of first octet is [240, 254], then IP Address belongs to class E.
Point-02:
For any given IP Address,
- IP Address of its network is obtained by setting all its Host ID part bits to 0.
Point-03:
For any given IP Address,
- Direct Broadcast Address is obtained by setting all its Host ID part bits to 1.
Point-04:
- For any given IP Address, limited Broadcast Address is obtained by setting all its bits to 1.
- For any network, its limited broadcast address is always 255.255.255.255
Point-05:
- Class D IP Addresses are not divided into Net ID and Host ID parts.
- Class E IP Addresses are not divided into Net ID and Host ID parts.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON IP ADDRESS IN NETWORKING-
Problem-01:
For the following IP Addresses-
- 1.2.3.4
- 10.15.20.60
- 130.1.2.3
- 150.0.150.150
- 200.1.10.100
- 220.15.1.10
- 250.0.1.2
- 300.1.2.3
Identify the Class, Network IP Address, Direct broadcast address and Limited broadcast address of each IP Address.
Solution-
Part-A:
Given IP Address is-
1.2.3.4
- IP Address belongs to class A
- Network IP Address = 1.0.0.0
- Direct Broadcast Address = 1.255.255.255
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
Part-B:
Given IP Address is-
10.15.20.60
- IP Address belongs to class A
- Network IP Address = 10.0.0.0
- Direct Broadcast Address = 10.255.255.255
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
Part-C:
Given IP Address is-
130.1.2.3
- IP Address belongs to class B
- Network IP Address = 130.1.0.0
- Direct Broadcast Address = 130.1.255.255
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
Part-D:
Given IP Address is-
150.0.150.150
- IP Address belongs to class B
- Network IP Address = 150.0.0.0
- Direct Broadcast Address = 150.0.255.255
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
Part-E:
Given IP Address is-
200.1.10.100
- IP Address belongs to class C
- Network IP Address = 200.1.10.0
- Direct Broadcast Address = 200.1.10.255
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
Part-F:
Given IP Address is-
220.15.1.10
- IP Address belongs to class C
- Network IP Address = 220.15.1.0
- Direct Broadcast Address = 220.15.1.255
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
Part-G:
Given IP Address is-
250.0.1.2
- IP Address belongs to class E
- Network IP Address = Not available
- Direct Broadcast Address = Not available
- Limited Broadcast Address = Not available
Part-H:
Given IP Address is-
300.1.2.3
- This is not a valid IP Address.
- This is because for any given IP Address, the range of its first octet is always [1, 254].
- First and Last IP Addresses are reserved.
Problem-02:
A device has two or more IP Addresses, the device is called-
- Workstation
- Router
- Gateway
- All of these
Solution-
- All the given devices have a network layer.
- So, they will have at least one IP Address.
In TCP/IP suite-
- Workstation and gateway have all the 5 layers.
- Router has only 3 layers last layer being network layer.
Workstation-
- A user may configure more than one IP Addresses in his workstation / computer.
- With more than one IP Address, it remains present in more than one networks.
- So, if one network goes down, it is always reachable from other networks.
The following figure shows a host present in more than one networks-
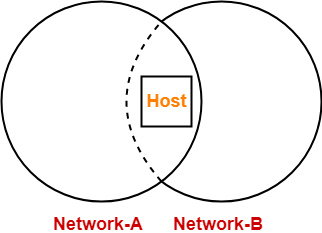
- It is important to note that IP Addresses are assigned to interfaces.
- When we buy a new laptop, we usually get 2-3 interfaces.
- Thus, a workstation can have more than one IP Addresses.
Router-
- A router may be connected to various interfaces.
- Each interface has a unique IP Address.
- Thus, a router may also have more than IP Addresses.
- Similar is the case with gateways because gateways are extension of routers.
Thus, Option (D) is correct.
Problem-03:
A host with IP Address 200.100.1.1 wants to send a packet to all the hosts in the same network.
What will be-
- Source IP Address
- Destination IP Address
Solution-
- Source IP Address = IP Address of the sender = 200.100.1.1
- Destination IP Address = Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
Problem-04:
A host with IP Address 10.100.100.100 wants to use loop back testing.
What will be-
- Source IP Address
- Destination IP Address
Solution-
- Source IP Address = 10.100.100.100
- Destination IP Address = Loopback Testing Address = 127.0.0.1
Problem-05:
How many bits are allocated for Network ID and Host ID in 23.192.157.234 address?
Solution-
Given IP Address belongs to class A.
Thus,
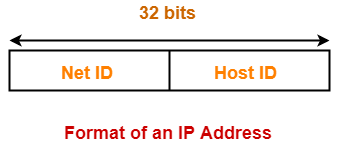
- Number of bits reserved for Network ID = 8
- Number of bits reserved for Host ID = 24
Problem-06:
Which devices can use logical addressing system?
- Hub
- Switch
- Bridge
- Router
Solution-
- Devices which have network layer as the last layer can only use logical addressing system.
- Devices which have data link layer as the last layer can only use physical addressing system.
- IP Addresses are the logical addresses and MAC Addresses are the physical addresses.
Option-A:
- Hub can neither use physical addressing system nor logical addressing system.
- This is because it has physical layer as the last layer.
Option-B:
- Switch can use physical addressing system but not logical addressing system.
- This is because it has data link layer as the last layer.
Option-C:
- Bridge can use physical addressing system but not logical addressing system.
- This is because it has data link layer as the last layer.
Option-D:
- Router can use physical addressing system as well as logical addressing system.
- This is because it has network layer as the last layer.
Thus, option (D) is correct.
Problem-07:
What is the network ID of the IP Address 230.100.123.70?
Solution-
- Given IP Address belongs to class D.
- Class D IP Addresses are not divided into the Network ID and Host ID parts.
- Thus, there is no network ID for the given IP Address.
Problem-08:
Match the following-
Column-I:
- 200.10.192.100
- 7.10.230.1
- 128.1.1.254
- 255.255.255.255
- 100.255.255.255
Column-II:
- Class A
- Limited Broadcast Address
- Direct Broadcast Address
- Class C
- Class B
Solution-
(I, D), (II, A), (III, E), (IV, B), (V, C)
Problem-09:
Suppose that instead of using 16 bits for network part of a class B Address, 20 bits have been used. How many class B networks would have been possible?
Solution-
- Total 20 bits are used for Network ID of class B.
- The first two bits are always set to 10.
- Then, with 18 bits, number of networks possible = 218
Problem-10:
What is the default mask for 192.0.46.10?
Solution-
- Given IP Address belongs to class C.
- For class C, default mask = 255.255.255.0
Next Article- Classless Addressing
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.