Contiguous Memory Allocation-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous articles on Static Partitioning and Dynamic Partitioning.
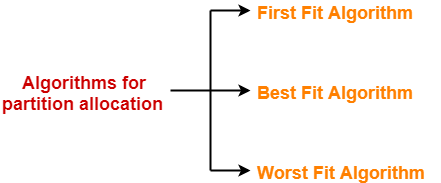
There are two popular techniques used for contiguous memory allocation-
In this article, we will discuss practice problems based on Contiguous Memory Allocation.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON CONTIGUOUS MEMORY ALLOCATION-
Problem-01:
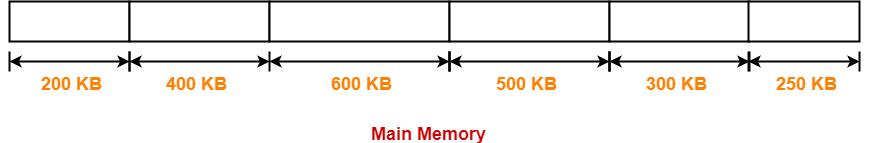
Consider six memory partitions of size 200 KB, 400 KB, 600 KB, 500 KB, 300 KB and 250 KB. These partitions need to be allocated to four processes of sizes 357 KB, 210 KB, 468 KB and 491 KB in that order.
Perform the allocation of processes using-
- First Fit Algorithm
- Best Fit Algorithm
- Worst Fit Algorithm
Solution-
According to question,
The main memory has been divided into fixed size partitions as-
Let us say the given processes are-
- Process P1 = 357 KB
- Process P2 = 210 KB
- Process P3 = 468 KB
- Process P4 = 491 KB
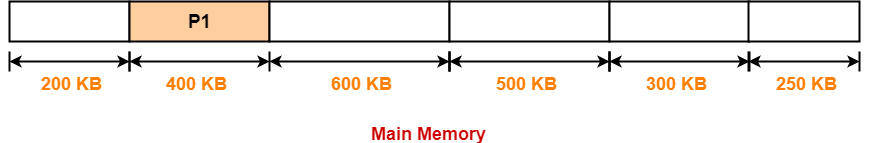
Allocation Using First Fit Algorithm-
In First Fit Algorithm,
- Algorithm starts scanning the partitions serially.
- When a partition big enough to store the process is found, it allocates that partition to the process.
The allocation of partitions to the given processes is shown below-
Step-01:
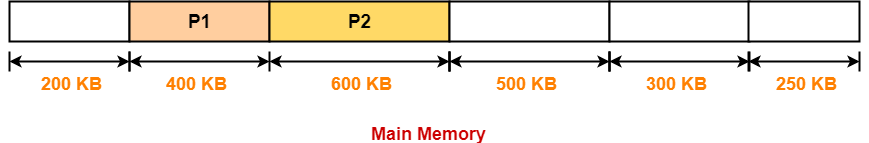
Step-02:
Step-03:
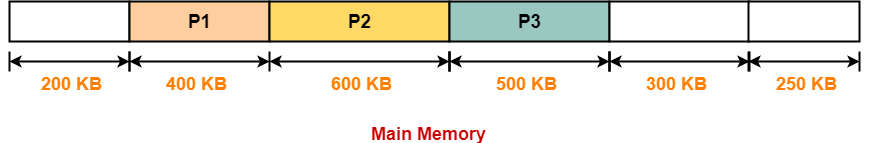
Step-04:
- Process P4 can not be allocated the memory.
- This is because no partition of size greater than or equal to the size of process P4 is available.
Allocation Using Best Fit Algorithm-
In Best Fit Algorithm,
- Algorithm first scans all the partitions.
- It then allocates the partition of smallest size that can store the process.
The allocation of partitions to the given processes is shown below-
Step-01:
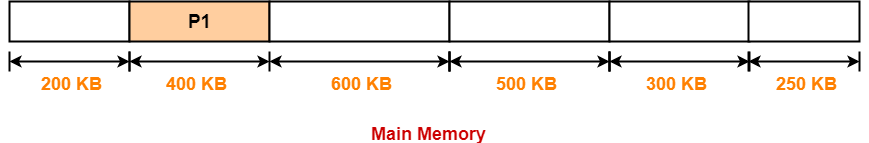
Step-02:
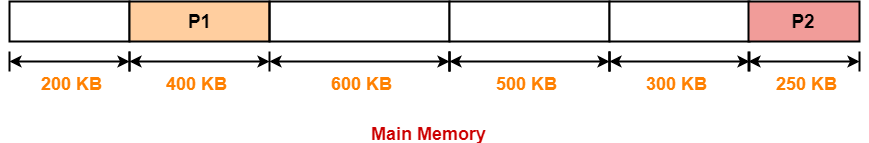
Step-03:
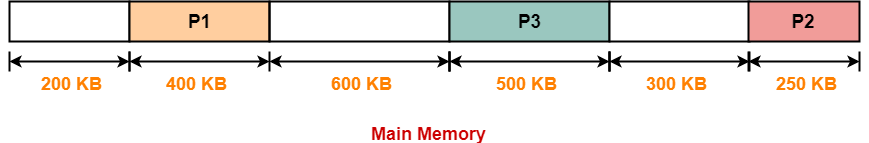
Step-04:
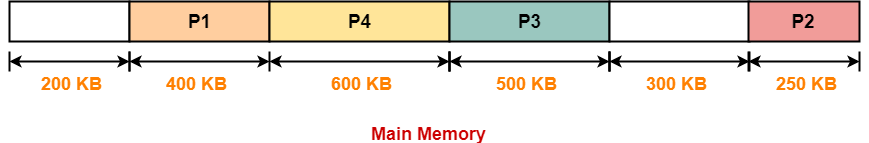
Allocation Using Worst Fit Algorithm-
In Worst Fit Algorithm,
- Algorithm first scans all the partitions.
- It then allocates the partition of largest size to the process.
The allocation of partitions to the given processes is shown below-
Step-01:
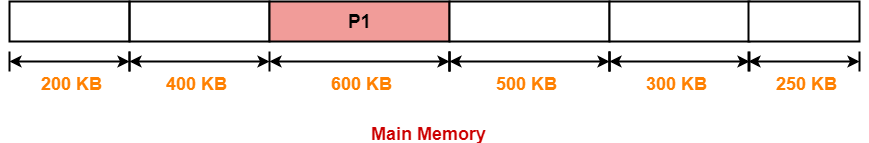
Step-02:
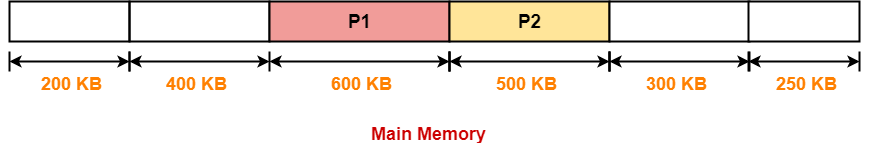
Step-03:
- Process P3 and Process P4 can not be allocated the memory.
- This is because no partition of size greater than or equal to the size of process P3 and process P4 is available.
To watch video solution, click here.
Problem-02:
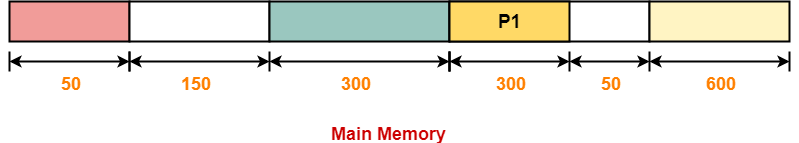
Consider the following heap (figure) in which blank regions are not in use and hatched regions are in use-
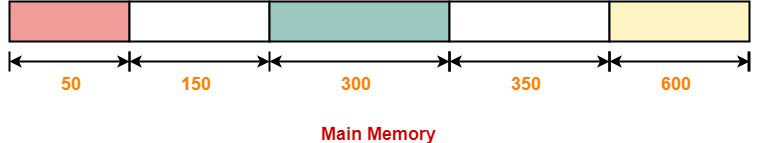
The sequence of requests for blocks of size 300, 25, 125, 50 can be satisfied if we use-
- Either first fit or best fit policy (any one)
- First fit but not best fit policy
- Best fit but not first fit policy
- None of the above
Solution-
The allocation follows variable size partitioning scheme.
Let us say the given processes are-
- Process P1 = 300 units
- Process P2 = 25 units
- Process P3 = 125 units
- Process P4 = 50 units
Allocation Using First Fit Algorithm-
The allocation of partitions to the given processes is shown below-
Step-01:
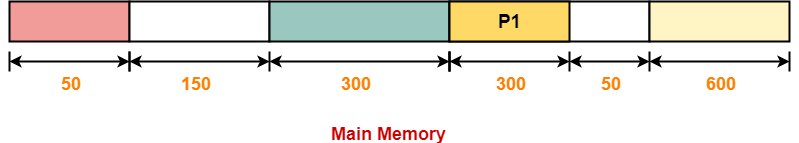
Step-02:
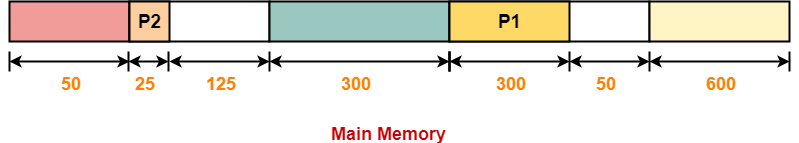
Step-03:
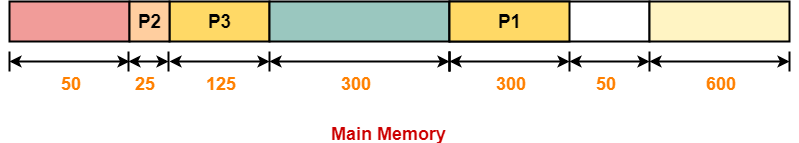
Step-04:
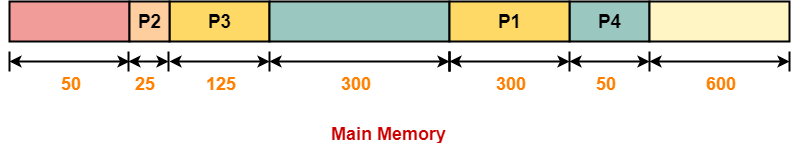
Allocation Using Best Fit Algorithm-
The allocation of partitions to the given processes is shown below-
Step-01:
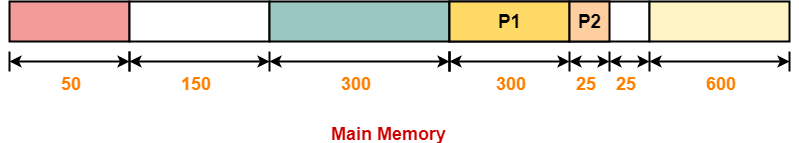
Step-02:
Step-03:
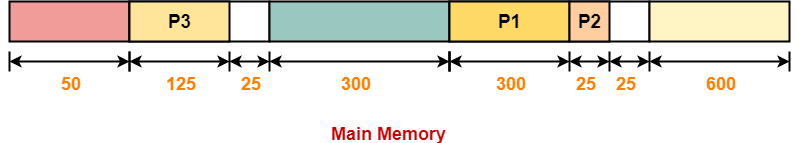
Step-04:
- Process P4 can not be allocated the memory.
- This is because no partition of size greater than or equal to the size of process P4 is available.
Thus,
- Only first fit allocation policy succeeds in allocating memory to all the processes.
- Option (B) is correct.
To watch video solution, click here.
Next Article- Introduction to Paging
Get more notes and other study material of Operating System.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.