A* Algorithm-
- A* Algorithm is one of the best and popular techniques used for path finding and graph traversals.
- A lot of games and web-based maps use this algorithm for finding the shortest path efficiently.
- It is essentially a best first search algorithm.
Working-
A* Algorithm works as-
- It maintains a tree of paths originating at the start node.
- It extends those paths one edge at a time.
- It continues until its termination criterion is satisfied.
A* Algorithm extends the path that minimizes the following function-
f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
Here,
- ‘n’ is the last node on the path
- g(n) is the cost of the path from start node to node ‘n’
- h(n) is a heuristic function that estimates cost of the cheapest path from node ‘n’ to the goal node
Algorithm-
- The implementation of A* Algorithm involves maintaining two lists- OPEN and CLOSED.
- OPEN contains those nodes that have been evaluated by the heuristic function but have not been expanded into successors yet.
- CLOSED contains those nodes that have already been visited.
The algorithm is as follows-
Step-01:
- Define a list OPEN.
- Initially, OPEN consists solely of a single node, the start node S.
Step-02:
If the list is empty, return failure and exit.
Step-03:
- Remove node n with the smallest value of f(n) from OPEN and move it to list CLOSED.
- If node n is a goal state, return success and exit.
Step-04:
Expand node n.
Step-05:
- If any successor to n is the goal node, return success and the solution by tracing the path from goal node to S.
- Otherwise, go to Step-06.
Step-06:
For each successor node,
- Apply the evaluation function f to the node.
- If the node has not been in either list, add it to OPEN.
Step-07:
Go back to Step-02.
AI algorithms will differ based on their applications. For a better understanding of how AI algorithms work in coding, the Github Certification course offers skills to learn how AI algorithms are used to analyze code, identify bugs, etc.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON A* ALGORITHM-
Problem-01:
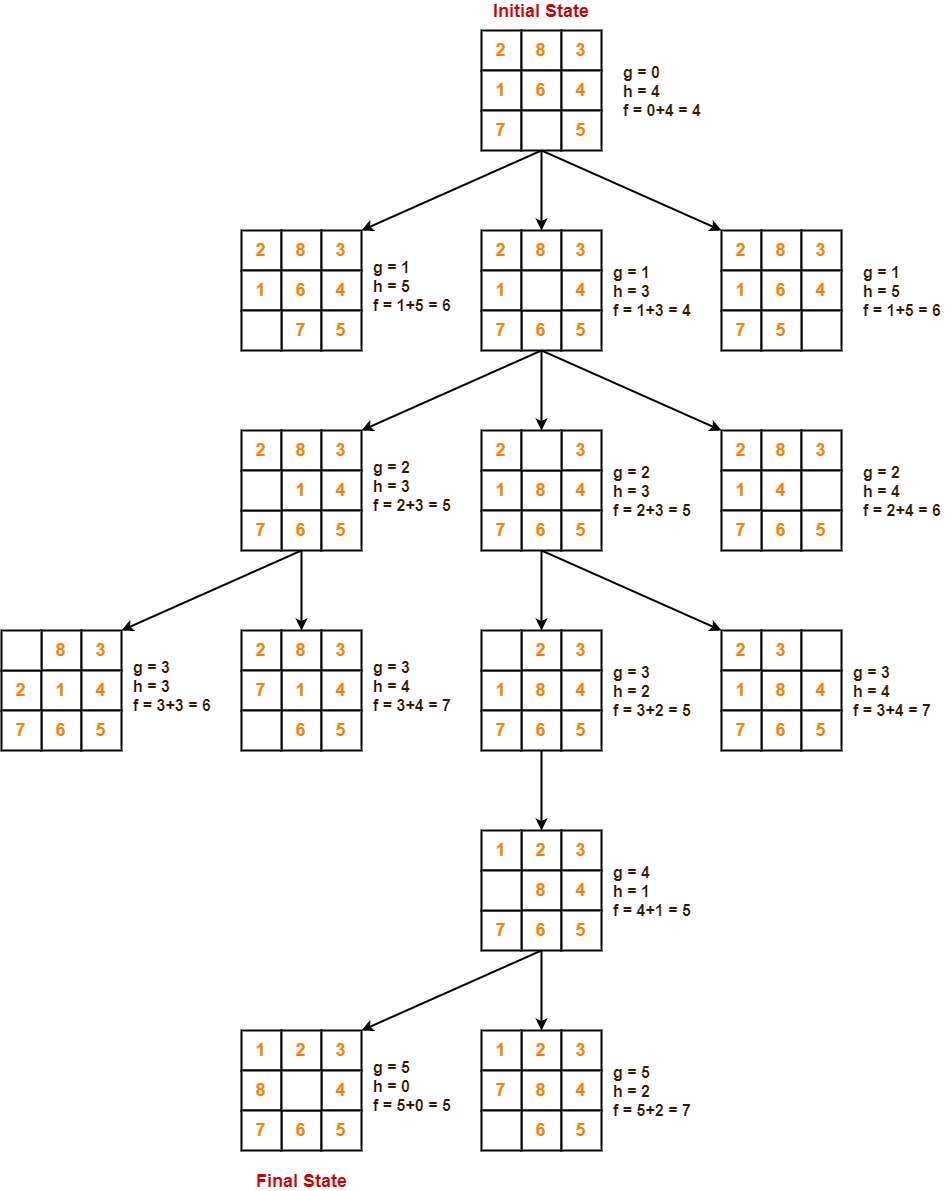
Given an initial state of a 8-puzzle problem and final state to be reached-

Find the most cost-effective path to reach the final state from initial state using A* Algorithm.
Consider g(n) = Depth of node and h(n) = Number of misplaced tiles.
Solution-
- A* Algorithm maintains a tree of paths originating at the initial state.
- It extends those paths one edge at a time.
- It continues until final state is reached.
Problem-02:
Consider the following graph-
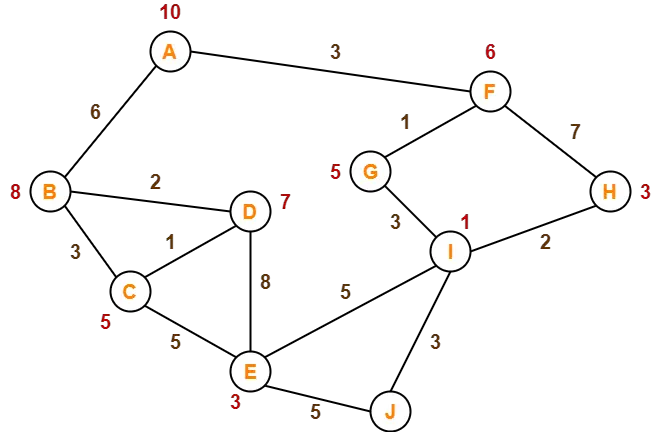
The numbers written on edges represent the distance between the nodes.
The numbers written on nodes represent the heuristic value.
Find the most cost-effective path to reach from start state A to final state J using A* Algorithm.
Solution-
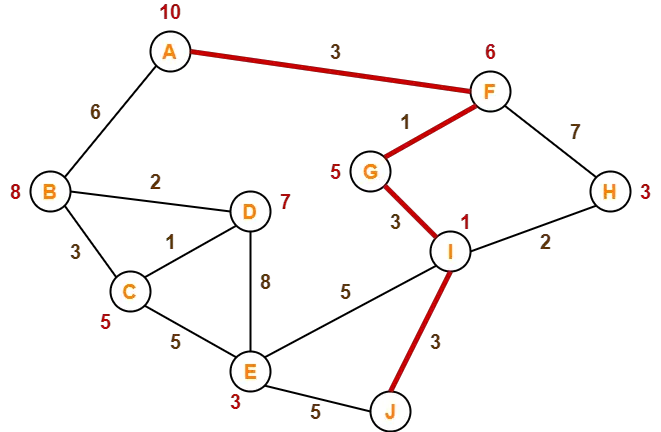
Step-01:
- We start with node A.
- Node B and Node F can be reached from node A.
A* Algorithm calculates f(B) and f(F).
- f(B) = 6 + 8 = 14
- f(F) = 3 + 6 = 9
Since f(F) < f(B), so it decides to go to node F.
Path- A → F
Step-02:
Node G and Node H can be reached from node F.
A* Algorithm calculates f(G) and f(H).
- f(G) = (3+1) + 5 = 9
- f(H) = (3+7) + 3 = 13
Since f(G) < f(H), so it decides to go to node G.
Path- A → F → G
Step-03:
Node I can be reached from node G.
A* Algorithm calculates f(I).
f(I) = (3+1+3) + 1 = 8
It decides to go to node I.
Path- A → F → G → I
Step-04:
Node E, Node H and Node J can be reached from node I.
A* Algorithm calculates f(E), f(H) and f(J).
- f(E) = (3+1+3+5) + 3 = 15
- f(H) = (3+1+3+2) + 3 = 12
- f(J) = (3+1+3+3) + 0 = 10
Since f(J) is least, so it decides to go to node J.
Path- A → F → G → I → J
This is the required shortest path from node A to node J.
Important Note-
It is important to note that-
- A* Algorithm is one of the best path finding algorithms.
- But it does not produce the shortest path always.
- This is because it heavily depends on heuristics.
To gain better understanding about A* Search Algorithm,
Get more notes and other study material of Artificial Intelligence.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.
