Application Layer Protocols-
Important application layer protocols are-
- Domain Name Service (DNS)
- Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
- Post Office Protocol (POP)
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
In this article, we will discuss about Post Office Protocol (POP).
Post Office Protocol-
- POP is short for Post Office Protocol.
- It is an application layer protocol.
Purpose-
- It is a message access protocol.
- It enables the clients to receive or download the emails from their remote mail server.
- POP version 3 (POP3) is the most popularly used version.
Working-
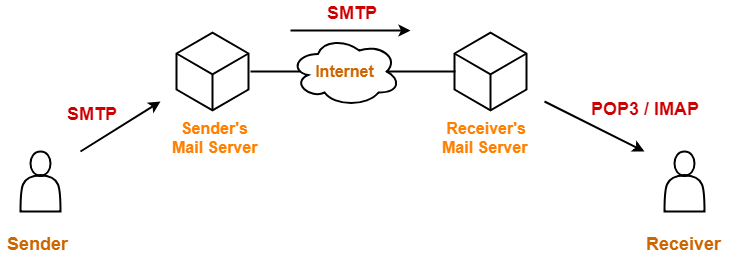
To retrieve a message from the mail server-
- Client establishes a TCP connection using port 110.
- Client identifies itself to the server.
- Client issues a series of POP3 commands.
Characteristics of POP-
- POP is a pull protocol.
- POP uses TCP at the transport layer.
- POP uses port number 110.
- POP uses persistent TCP connections.
- POP is a connection oriented protocol.
- POP is an in-band protocol.
- POP is a stateful protocol until the mail is downloaded as well as stateless across sessions.
Internet Message Access Protocol-
- IMAP is short for Internet Message Access Protocol.
- It is an application layer protocol.
- It also enables the clients to receive or download the emails from their remote mail server.
| POP has been largely superseded by Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP). |
Characteristics of IMAP-
- IMAP is a pull protocol.
- IMAP uses TCP at the transport layer.
- IMAP uses port number 143.
- IMAP uses persistent TCP connections.
- IMAP is a connection oriented protocol.
- IMAP is an in-band protocol.
- IMAP is a stateful protocol.
- IMAP distributes mail boxes across multiple servers.
POP Vs IMAP-
The following table lists the differences between POP and IMAP-
| Post Office Protocol | Internet Message Access Protocol |
| POP allows you to read the mail only after downloading it. | IMAP allows you to check the mail content before downloading.
So, with IMAP you can choose to download your messages or just delete them. |
| The email message is downloaded to the local computer and the copy at the server is deleted. | The email message is stored on the mail server itself. |
| The user can not organize mails in the mail box of the mail server. | The user can organize mails on the server. |
| Mails can only be accessed from a single device. | Mails can be accessed from multiple devices which is the biggest advantage. |
| In POP, the mail server and client’s mail account are not synced.
So, changes made in the client’s mail account are not visible on the web mail inbox.
Example-
If you are using POP and marks a mail as read, it does not get marked as read in the web mail inbox because the mails are downloaded to the computer and so the changes won’t be visible on the server. |
In IMAP, the mail server and the client’s mail account are synced.
So, changes made in the client’s mail account are instantly visible on the web mail inbox.
Example-
If you are using IMAP and marks a mail as read, it gets marked as read in the web mail inbox too because the changes are taking place on the server. |
| POP is a stateful protocol until the mail is downloaded as well as stateless across sessions. | IMAP is a stateful protocol because the IMAP server has to maintain a folder hierarchy for each of its users. |
| POP is a better choice for those who hardly checks their mail on any other computer. | IMAP is a better choice for those who frequently check their mails on other computers. |
To gain better understanding about POP Protocol and IMAP Protocol,
Next Article- File Transfer Protocol | FTP
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.