IP Address in Networking-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on IP Address.
We have discussed-
- IP Address is a 32 bit address that uniquely identifies each device on the network.
- It is assigned by ISP to each device present on its network.
In this article, we will discuss about casting.
Casting in Networking-
| Transmitting data (stream of packets) over the network is termed as casting. |
Types Of Casting-
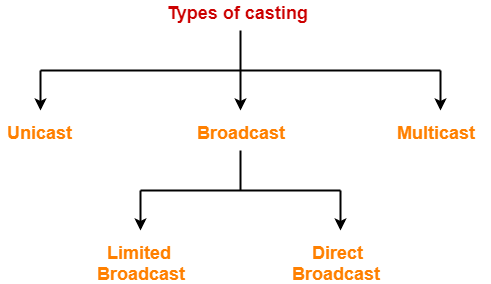
- Unicast
- Broadcast
- Multicast
1. Unicast-
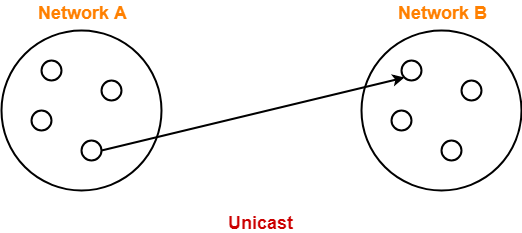
- Transmitting data from one source host to one destination host is called as unicast.
- It is a one to one transmission.
Example-
Host A having IP Address 11.1.2.3 sending data to host B having IP Address 20.12.4.2.
Here,
- Source Address = IP Address of host A = 11.1.2.3
- Destination Address = IP Address of host B = 20.12.4.2
2. Broadcast-
- Transmitting data from one source host to all other hosts residing in the same or other network is called as broadcast.
- It is a one to all transmission.
Based on recipient’s network, it is classified as-
- Limited Broadcast
- Direct Broadcast
A. Limited Broadcast-
- Transmitting data from one source host to all other hosts residing in the same network is called as limited broadcast.
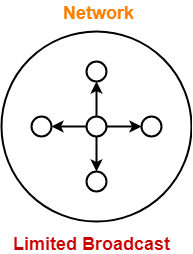
NOTELimited Broadcast Address for any network = All 32 bits set to 1 = 11111111.11111111.11111111.11111111 = 255.255.255.255 |
Example-
Host A having IP Address 11.1.2.3 sending data to all other hosts residing in the same network.
Here,
- Source Address = IP Address of host A = 11.1.2.3
- Destination Address = 255.255.255.255
B. Direct Broadcast-
- Transmitting data from one source host to all other hosts residing in some other network is called as direct broadcast.
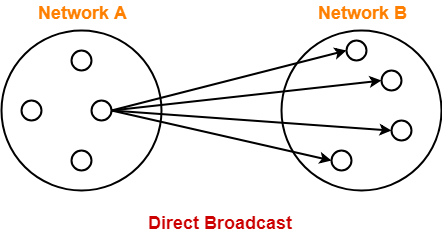
NOTEDirect Broadcast Address for any network is the IP Address where-
|
Example-
Host A having IP Address 11.1.2.3 sending data to all other hosts residing in the network having IP Address 20.0.0.0
Here,
- Source Address = IP Address of host A = 11.1.2.3
- Destination Address = 20.255.255.255
3. Multicast-
- Transmitting data from one source host to a particular group of hosts having interest in receiving the data is called as multicast.
- It is a one to many transmission.

Examples-
- Sending a message to a particular group of people on whatsapp
- Sending an email to a particular group of people
- Video conference or teleconference
MAC Address Vs IP Address-
The following table summarizes the differences between MAC Address and IP Address-
| MAC Address | IP Address |
| It stands for Media Access Control Address. | It stands for Internet Protocol Address. |
| MAC Address identifies the physical address of a computer on the internet. | IP Address identifies the connection of a computer on the internet. |
| Manufacturer of NIC card assigns the MAC Address. | Network Administrator or ISP assigns the IP Address. |
| Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) is used for resolving physical (MAC) Address into IP address. | Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used for resolving IP Address into physical (MAC) address. |
NOTE-
- Multicast makes use of IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) to identify its group.
- Each group is assigned with an IP Address from class D of IPv4.
To gain better understanding about Unicast Broadcast Multicast,
Next Article- Practice Problems On IP Address
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.