Error Detection in Computer Networks-
When sender transmits data to the receiver, the data might get scrambled by noise or data might get corrupted during the transmission.
| Error detection is a technique that is used to check if any error occurred in the data during the transmission. |
Error Detection Methods-
Some popular error detection methods are-
- Single Parity Check
- Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
- Checksum
In this article, we will discuss about Single Parity Check.
Single Parity Check-
In this technique,
- One extra bit called as parity bit is sent along with the original data bits.
- Parity bit helps to check if any error occurred in the data during the transmission.
Steps Involved-
Error detection using single parity check involves the following steps-
Step-01:
At sender side,
- Total number of 1’s in the data unit to be transmitted is counted.
- The total number of 1’s in the data unit is made even in case of even parity.
- The total number of 1’s in the data unit is made odd in case of odd parity.
- This is done by adding an extra bit called as parity bit.
Step-02:
- The newly formed code word (Original data + parity bit) is transmitted to the receiver.
Step-03:
At receiver side,
- Receiver receives the transmitted code word.
- The total number of 1’s in the received code word is counted.
Then, following cases are possible-
- If total number of 1’s is even and even parity is used, then receiver assumes that no error occurred.
- If total number of 1’s is even and odd parity is used, then receiver assumes that error occurred.
- If total number of 1’s is odd and odd parity is used, then receiver assumes that no error occurred.
- If total number of 1’s is odd and even parity is used, then receiver assumes that error occurred.
Parity Check Example-
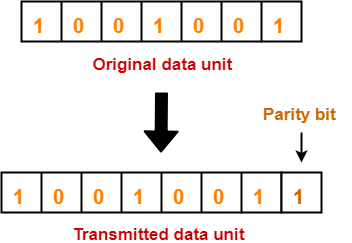
Consider the data unit to be transmitted is 1001001 and even parity is used.
Then,
At Sender Side-
- Total number of 1’s in the data unit is counted.
- Total number of 1’s in the data unit = 3.
- Clearly, even parity is used and total number of 1’s is odd.
- So, parity bit = 1 is added to the data unit to make total number of 1’s even.
- Then, the code word 10010011 is transmitted to the receiver.
At Receiver Side-
- After receiving the code word, total number of 1’s in the code word is counted.
- Consider receiver receives the correct code word = 10010011.
- Even parity is used and total number of 1’s is even.
- So, receiver assumes that no error occurred in the data during the transmission.
Advantage-
- This technique is guaranteed to detect an odd number of bit errors (one, three, five and so on).
- If odd number of bits flip during transmission, then receiver can detect by counting the number of 1’s.
Also Read- Checksum
Limitation-
- This technique can not detect an even number of bit errors (two, four, six and so on).
- If even number of bits flip during transmission, then receiver can not catch the error.
EXAMPLE
|
To gain better understanding about single parity check,
Next Article- Cyclic Redundancy Check
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.