Binary Search Tree-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Binary Search Trees.
Binary search tree (BST) is a special kind of binary tree where each node contains-
- Only larger values in its right subtree.
- Only smaller values in its left subtree.
In this article, we will discuss about Binary Search Tree Traversal.
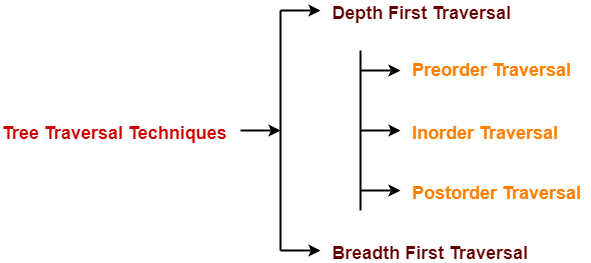
BST Traversal-
- A binary search tree is traversed in exactly the same way a binary tree is traversed.
- In other words, BST traversal is same as binary tree traversal.
Read More- Binary Tree Traversal
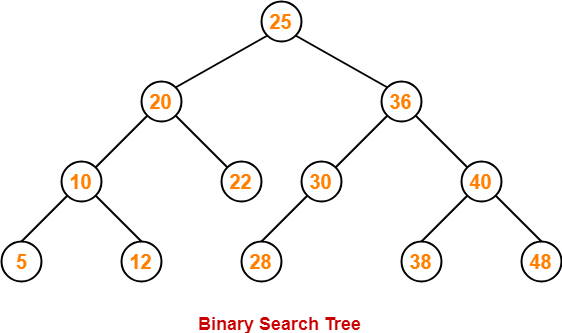
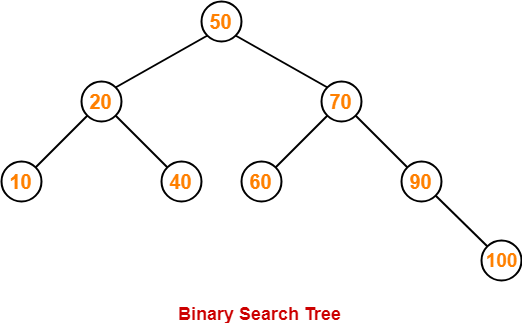
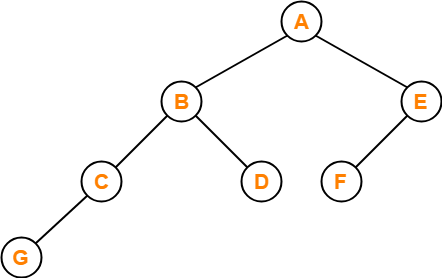
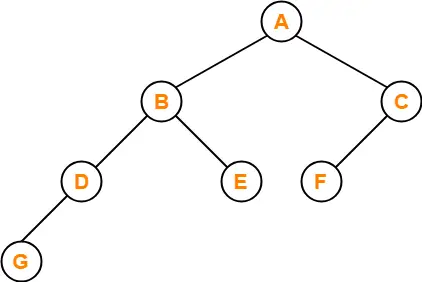
Example-
Consider the following binary search tree-
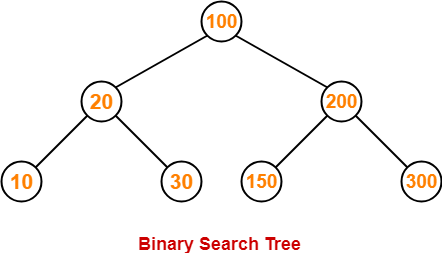
Now, let us write the traversal sequences for this binary search tree-
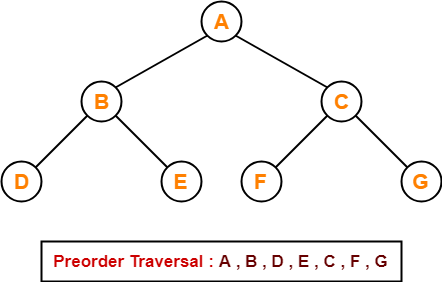
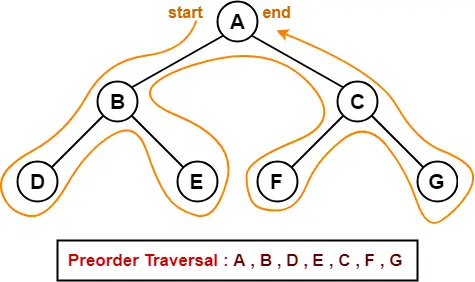
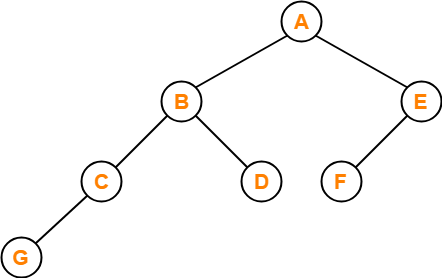
Preorder Traversal-
100 , 20 , 10 , 30 , 200 , 150 , 300
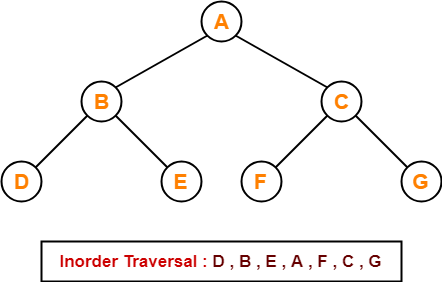
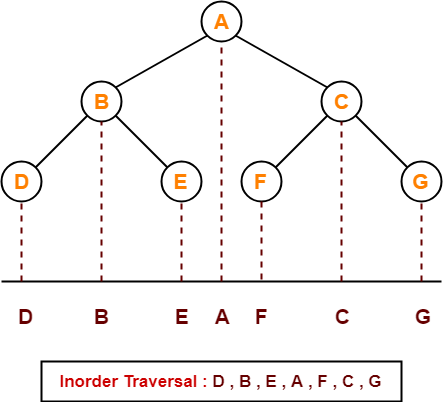
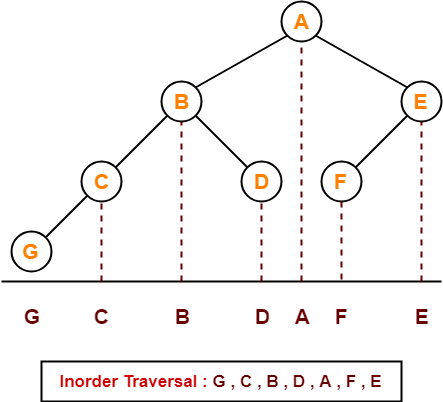
Inorder Traversal-
10 , 20 , 30 , 100 , 150 , 200 , 300
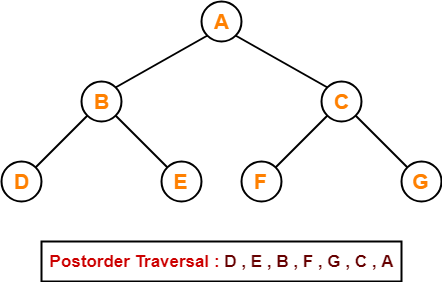
Postorder Traversal-
10 , 30 , 20 , 150 , 300 , 200 , 100
Important Notes-
Note-01:
- Inorder traversal of a binary search tree always yields all the nodes in increasing order.
Note-02:
Unlike Binary Trees,
- A binary search tree can be constructed using only preorder or only postorder traversal result.
- This is because inorder traversal can be obtained by sorting the given result in increasing order.
To gain better understanding about Binary Search Tree Traversal,
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON BST TRAVERSAL-
Problem-01:
Suppose the numbers 7 , 5 , 1 , 8 , 3 , 6 , 0 , 9 , 4 , 2 are inserted in that order into an initially empty binary search tree. The binary search tree uses the usual ordering on natural numbers.
What is the inorder traversal sequence of the resultant tree?
- 7 , 5 , 1 , 0 , 3 , 2 , 4 , 6 , 8 , 9
- 0 , 2 , 4 , 3 , 1 , 6 , 5 , 9 , 8 , 7
- 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9
- 9 , 8 , 6 , 4 , 2 , 3 , 0 , 1 , 5 , 7
Solution-
This given problem may be solved in the following two ways-
Method-01:
- We construct a binary search tree for the given elements.
- We write the inorder traversal sequence from the binary search tree so obtained.
Following these steps, we have-
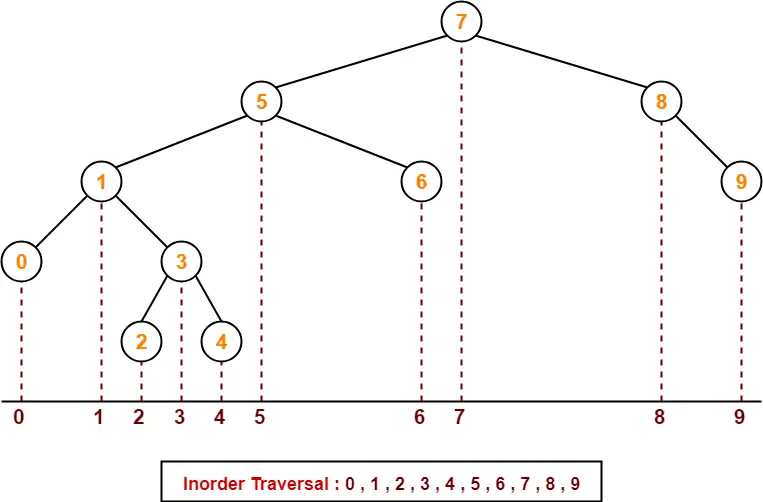
Thus, Option (C) is correct.
Method-02:
We know, inorder traversal of a binary search tree always yields all the nodes in increasing order.
Using this result,
- We arrange all the given elements in increasing order.
- Then, we report the sequence so obtained as inorder traversal sequence.
|
Inorder Traversal :
0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 |
Thus, Option (C) is correct.
Problem-02:
The preorder traversal sequence of a binary search tree is-
30 , 20 , 10 , 15 , 25 , 23 , 39 , 35 , 42
What one of the following is the postorder traversal sequence of the same tree?
- 10 , 20 , 15 , 23 , 25 , 35 , 42 , 39 , 30
- 15 , 10 , 25 , 23 , 20 , 42 , 35 , 39 , 30
- 15 , 20 , 10 , 23 , 25 , 42 , 35 , 39 , 30
- 15 , 10 , 23 , 25 , 20 , 35 , 42 , 39 , 30
Solution-
In this question,
- We are provided with the preorder traversal sequence.
- We write the inorder traversal sequence by arranging all the numbers in ascending order.
Then-
- Postorder Traversal : 30 , 20 , 10 , 15 , 25 , 23 , 39 , 35 , 42
- Inorder Traversal : 10 , 15 , 20 , 23 , 25 , 30 , 35 , 39 , 42
Now,
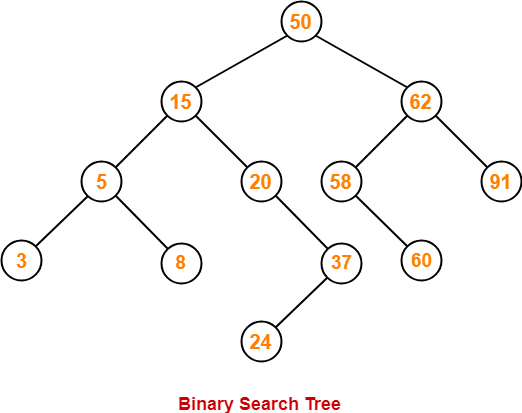
- We draw a binary search tree using these traversal results.
- The binary search tree so obtained is as shown-
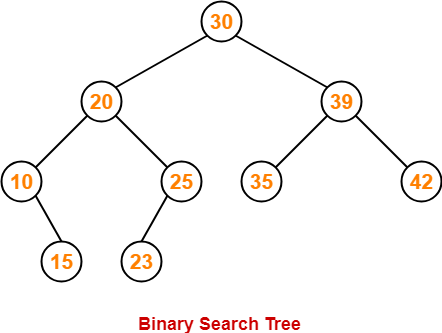
Now, we write the postorder traversal sequence-
|
Postorder Traversal :
15 , 10 , 23 , 25, 20, 35, 42, 39, 30 |
Thus, Option (D) is correct.
To watch video solutions and practice more problems,
Download Handwritten Notes Here-
Next Article- Binary Search Tree Operations
Get more notes and other study material of Data Structures.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.