Transaction in DBMS-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Transactions in DBMS.
We have discussed-
- A transaction is a set of logically related operations.
- A transaction goes through different states throughout its life cycle.
- The life cycle of a transaction is-
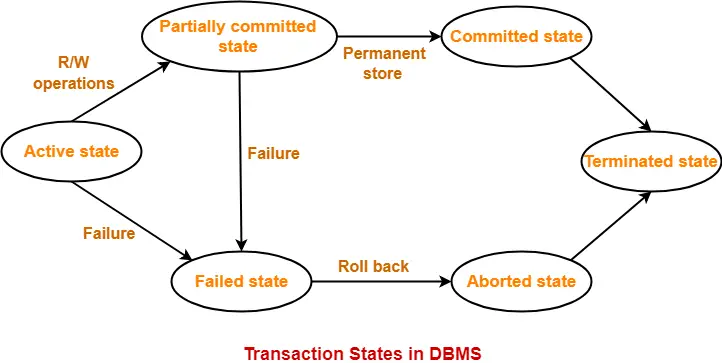
In this article, we will discuss ACID properties of a transaction.
ACID Properties-
- It is important to ensure that the database remains consistent before and after the transaction.
- To ensure the consistency of database, certain properties are followed by all the transactions occurring in the system.
- These properties are called as ACID Properties of a transaction.
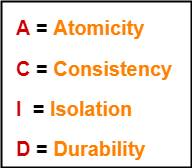
1. Atomicity-
- This property ensures that either the transaction occurs completely or it does not occur at all.
- In other words, it ensures that no transaction occurs partially.
- That is why, it is also referred to as “All or nothing rule“.
- It is the responsibility of Transaction Control Manager to ensure atomicity of the transactions.
2. Consistency-
- This property ensures that integrity constraints are maintained.
- In other words, it ensures that the database remains consistent before and after the transaction.
- It is the responsibility of DBMS and application programmer to ensure consistency of the database.
3. Isolation-
- This property ensures that multiple transactions can occur simultaneously without causing any inconsistency.
- During execution, each transaction feels as if it is getting executed alone in the system.
- A transaction does not realize that there are other transactions as well getting executed parallely.
- Changes made by a transaction becomes visible to other transactions only after they are written in the memory.
- The resultant state of the system after executing all the transactions is same as the state that would be achieved if the transactions were executed serially one after the other.
- It is the responsibility of concurrency control manager to ensure isolation for all the transactions.
4. Durability-
- This property ensures that all the changes made by a transaction after its successful execution are written successfully to the disk.
- It also ensures that these changes exist permanently and are never lost even if there occurs a failure of any kind.
- It is the responsibility of recovery manager to ensure durability in the database.
Next Article- Concurrency Problems in DBMS
Get more notes and other study material of Database Management System (DBMS).
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.