Machine Learning-
| Learning is a continuous process of improvement over experience. |
Machine learning is building machines that can adapt and learn from experience without being explicitly programmed.
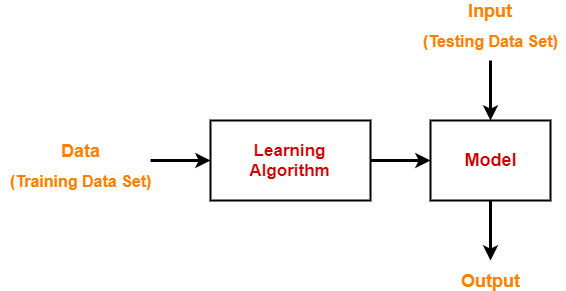
In machine learning,
- There is a learning algorithm.
- Data called as training data set is fed to the learning algorithm.
- Learning algorithm draws inferences from the training data set.
- It generates a model which is a function that maps input to the output.
Machine Learning Applications-
Some important applications of machine learning are-
- Spam Filtering
- Fraudulent Transactions
- Credit Scoring
- Recommendations
- Robot Navigation
Machine Learning Algorithms-
There are three types of machine learning algorithms-
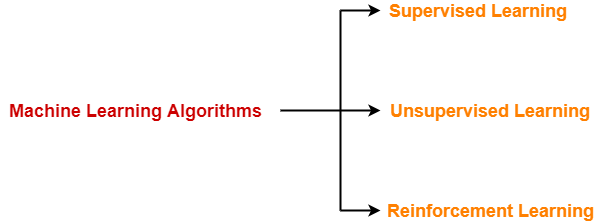
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
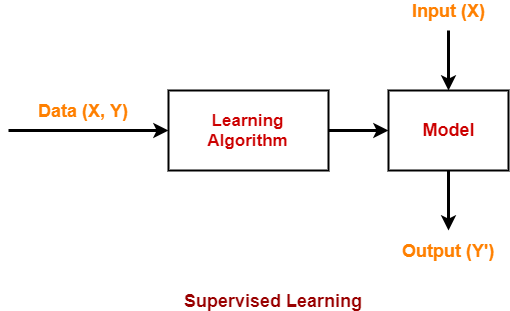
1. Supervised Learning-
In this type of machine learning algorithm,
- The training data set is a labeled data set.
- In other words, the training data set contains the input value (X) and target value (Y).
- The learning algorithm generates a model.
- Then, new data set consisting of only the input value is fed.
- The model then generates the target value based on its learning.
Example-
Consider a sample database consisting of two columns where-
- The first column specifies mails.
- The second column specifies whether those emails are spam or not.
| Mails (X) | IsSpam (Y) |
| Mail-1 | Yes |
| Mail-2 | No |
| Mail-3 | No |
| Mail-4 | No |
In this training data set, emails categorized as spam or not are done by a supervisor’s knowledge.
So, it is supervised learning algorithm.
Applications-
Some real-life applications are-
- Spam Filtering
- House Price Prediction
- Credit Scoring (high risk or a low risk customer while lending loans by the banks)
- Face Recognition etc
Types of Supervised Learning Algorithm-
There are two types of supervised learning algorithm-

- Regression
- Classification
Regression-
Here,
- The target variable (Y) has continuous value.
- Example- house price prediction
Classification-
Here,
- The target variable (Y) has discrete values such as Yes or No, 0 or 1 and many more.
- Example- Credit Scoring, Spam Filtering
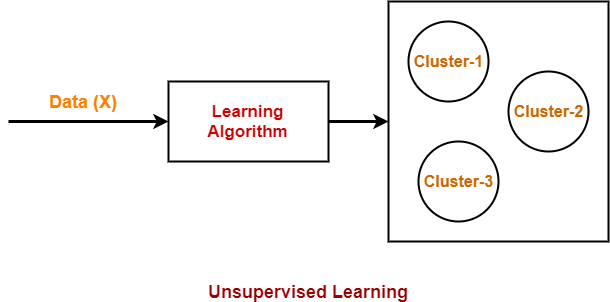
2. Unsupervised Learning-
In this type of machine learning algorithm,
- The training data set is an unlabeled data set.
- In other words, the training data set contains only the input value (X) and not the target value (Y).
- Based on the similarity between data, it tries to draw inference from the data such as finding patterns or clusters.
Applications-
Some real-life applications are-
- Document Clustering
- Finding fraudulent transactions
3. Reinforcement Learning-
In this type of machine learning algorithm,
- The agent acts in an environment in order to maximize the rewards and minimize the penalty.
- Unlike supervised learning, no data is provided to the agent.
- The agent itself takes action or sequence of actions whether right or wrong to perform a task and learn from the experience.
Applications-
Some real-life applications are-
- Game Playing
- Robot Navigation
To gain better understanding about Machine Learning & its Algorithms,
Next Article- Machine Learning Workflow
Get more notes and other study material of Machine Learning.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.