Referential Integrity Constraint-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Constraints in DBMS.
We have discussed-
- Relational constraints impose the restrictions on the database to ensure the correctness of data.
- There are following 5 different types of relational constraints-
- Referential Integrity constraint is enforced when a foreign key references the primary key of a relation.
- It specifies that all the values taken by the foreign key must either be available in the relation of the primary key or be null.
Also read- Foreign Key in DBMS
Referential Integrity Constraint Violation-
There are following three possible causes of violation of referential integrity constraint-
Cause-01: Insertion in a referencing relation
Cause-02: Deletion from a referenced relation
Cause-03: Updation in a referenced relation
Cause-01: Insertion in a Referencing Relation-
- It is allowed to insert only those values in the referencing attribute which are already present in the value of the referenced attribute.
- Inserting a value in the referencing attribute which is not present in the value of the referenced attribute violates the referential integrity constraint.
Example-
Consider the following two schemas-
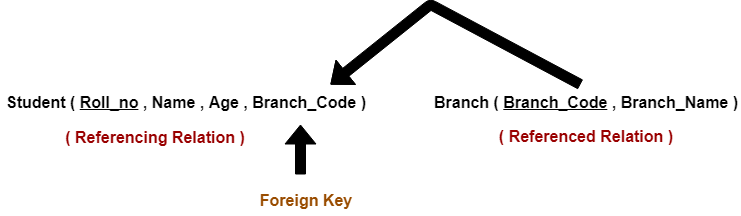
Here, relation “Student” references the relation “Branch”.
Student
| Roll_no | Name | Age | Branch_Code |
| 1 | Rahul | 22 | CS |
| 2 | Anjali | 21 | CS |
| 3 | Teena | 20 | IT |
Branch
| Branch_Code | Branch_Name |
| CS | Computer Science |
| EE | Electronics Engineering |
| IT | Information Technology |
| CE | Civil Engineering |
Here,
- In relation “Student”, we can not insert any student having branch code ME (Mechanical Engineering).
- This is because branch code ME is not present in the relation “Branch”.
Cause-02: Deletion from a Referenced Relation-
- It is not allowed to delete a row from the referenced relation if the referencing attribute uses the value of the referenced attribute of that row.
- Such a deletion violates the referential integrity constraint.
Example-
Consider the above two relations,
- We can not delete a tuple from the relation “Branch” having branch code ‘CS’.
- This is because the referencing attribute “Branch_Code” of the referencing relation “Student” references the value ‘CS’.
- However, we can safely delete a tuple from the relation “Branch” having branch code ‘CE’.
- This is because the referencing attribute “Branch_Code” of the referencing relation “Student” does not uses this value.
Handling the Violation-
The violation caused due to a deletion from the referenced relation can be handled in the following three ways-
Method-01:
- This method involves simultaneously deleting those tuples from the referencing relation where the referencing attribute uses the value of referenced attribute being deleted.
- This method of handling the violation is called as On Delete Cascade.
Method-02:
- This method involves aborting or deleting the request for a deletion from the referenced relation if the value is used by the referencing relation.
Method-03:
- This method involves setting the value being deleted from the referenced relation to NULL or some other value in the referencing relation if the referencing attribute uses that value.
Cause-03: Updation in a Referenced Relation-
- It is not allowed to update a row of the referenced relation if the referencing attribute uses the value of the referenced attribute of that row.
- Such an updation violates the referential integrity constraint.
Example-
Consider the above relation.
- We can not update a tuple in the relation “Branch” having branch code ‘CS’ to the branch code ‘CSE’.
- This is because referencing attribute “Branch_Code” of the referencing relation “Student” references the value ‘CS’.
Handling the Violation-
The violation caused due to an updation in the referenced relation can be handled in the following three ways-
Method-01:
- This method involves simultaneously updating those tuples of the referencing relation where the referencing attribute uses the referenced attribute value being updated.
- This method of handling the violation is called as On Update Cascade.
Method-02:
- This method involves aborting or deleting the request for an updation of the referenced relation if the value is used by the referencing relation.
Method-03:
- This method involves setting the value being updated in the referenced relation to NULL or some other value in the referencing relation if the referencing attribute uses that value.
Next Article- Closure of an Attribute Set
Get more notes and other study material of Database Management System (DBMS).
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.