Subnet Mask-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Subnet Mask.
We have discussed-
- Subnet mask is a 32 bit address consisting of a sequence of 1’s and 0’s.
- It is used to determine to which subnet the given IP Address belongs to.
In this article, we will discuss how subnet mask is used by the host assigned to it.
Concept To Know-
When any host connects to the internet, ISP provides following 4 things to the host-
- IP Address
- Default Gateway
- Subnet Mask
- DNS
1. IP Address-
- ISP assigns an IP Address to the host so that it can be uniquely identified on the Internet.
2. Default Gateway-
- Default router connected to the network in which the host is present is the default gateway for the host.
3. Subnet Mask-
- Subnet mask is a 32 bit number that is assigned to the host.
- It is used to determine to which network the given IP Address belongs to.
4. Domain Name Service (DNS)-
- Domain Name Service (DNS) is used to translate the domain name into an IP Address.
Subnet Mask Use-
| Subnet mask is used to determine to which network the given IP Address belongs to. |
- Host use its subnet mask to determine whether the other host it wants to communicate with is present within the same network or not.
- If the destination host is present within the same network, then source host sends the packet directly to the destination host.
- If the destination host is present in some other network, then source host routes the packet to the default gateway (router).
- Router then sends the packet to the destination host.
Example-
Consider-
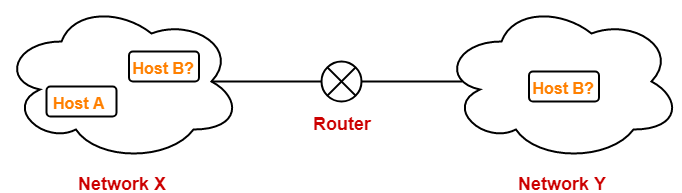
- There is a host A present in some network X.
- There is a host B.
- Host A wants to send a packet to host B.
Before transmitting the packet, host A determines whether host B is present within the same network or not.
Here,
- Host A = Source host
- Host B = Destination host
To determine whether destination host is present within the same network or not, source host follows the following steps-
Step-01:
- Source host computes its own network address using its own IP Address and subnet mask.
- After computation, source host obtains its network address with respect to itself.
Step-02:
- Source host computes the network address of destination host using destination IP Address and its own subnet mask.
- After computation, source host obtains the network address of destination host with respect to itself.
Step-03:
Source host compares the two results obtained in the above steps.
Then, following two cases are possible-
Case-01:
If the results are same,
- Source host assumes that the destination host is present within the same network.
- Source host sends the packet directly to the destination host.
Case-02:
If the results are different,
- Source host assumes that the destination host is present in some other network.
- Source host sends the packet via router to the destination host.
Important Points-
Note-01:
- Each host knows only its own subnet mask.
- It does not know the subnet mask of any other host.
Note-02:
- The conclusion drawn by a host about the presence of other host within the same or different network might be wrong.
Note-03:
- Consider host A draws some conclusion about host B.
- Then, same conclusion might not be drawn by host B about host A.
- Both the hosts have to perform the above procedure separately at their ends to conclude anything.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON USE OF SUBNET MASK-
Problem-01:
Two computers C1 and C2 are configured as follows-
- C1 has IP Address 203.197.2.53 and net mask 255.255.128.0
- C2 has IP Address 203.197.75.201 and net mask 255.255.192.0
Which one of the following statements is true?
- C1 and C2 both assume they are on the same network
- C2 assumes C1 is on same network but C1 assumes C2 is on a different network
- C1 assumes C2 is on same network but C2 assumes C1 is on a different network
- C1 and C2 both assume they are on different networks
Solution-
At Computer C1-
C1 computes its network address using its own IP Address and subnet mask as-
203.197.2.53 AND 255.255.128.0
= 203.197.0.0
C1 computes the network address of C2 using IP Address of C2 and its own subnet mask as-
203.197.75.201 AND 255.255.128.0
= 203.197.0.0
Since both the results are same, so C1 assumes that C2 is on the same network.
At Computer C2-
C2 computes its network address using its own IP Address and subnet mask as-
203.197.75.201 AND 255.255.192.0
= 203.197.64.0
C2 computes the network address of C1 using IP Address of C1 and its own subnet mask as-
203.197.2.53 AND 255.255.192.0
= 203.197.0.0
Since both the results are different, so C2 assumes that C1 is on a different network.
Thus, Option (C) is correct.
Problem-02:
The subnet mask for a particular network is 255.255.31.0. Which of the following pairs of IP Addresses could belong to this network?
- 172.57.88.62 and 172.56.87.233
- 10.35.28.2 and 10.35.29.4
- 191.203.31.87 and 191.234.31.88
- 128.8.129.43 and 128.8.161.55
Solution-
Let the given two IP Addresses belong to Host A and Host B.
Checking Option (A)-
- Host A IP Address = 172.57.88.62
- Host B IP Address = 172.56.87.233
At Host A-
Host A computes its network address using its own IP Address and subnet mask-
172.57.88.62 AND 255.255.31.0
= 172.57.24.0
Host A computes the network address of Host B using IP Address of Host B and its own subnet mask-
172.56.87.233 AND 255.255.31.0
= 172.56.23.0
Since both the results are different, so host A assumes that host B is on a different network.
Thus, both can’t belong to the same network.
Hence, this option gets eliminated.
Checking Option (B)-
- Host A IP Address = 10.35.28.2
- Host B IP Address = 10.35.29.4
At Host A-
Host A computes its network address using its own IP Address and subnet mask-
10.35.28.2 AND 255.255.31.0
= 10.35.28.0
Host A computes the network address of Host B using IP Address of Host B and its own subnet mask-
10.35.29.4 AND 255.255.31.0
= 10.35.29.0
Since both the results are different, so host A assumes that host B is on a different network.
Thus, both can’t belong to the same network.
Hence, this option gets eliminated.
Checking Option (C)-
- Host A IP Address = 191.203.31.87
- Host B IP Address = 191.234.31.88
At Host A-
Host A computes its network address using its own IP Address and subnet mask-
191.203.31.87 AND 255.255.31.0
= 191.203.31.0
Host A computes the network address of Host B using IP Address of Host B and its own subnet mask-
191.234.31.88 AND 255.255.31.0
= 191.234.31.0
Since both the results are same, so host A assumes that host B is on the same network.
At Host B-
Host B computes its network address using its own IP Address and subnet mask-
191.234.31.88 AND 255.255.31.0
= 191.234.31.0
Host B computes the network address of Host A using IP Address of Host A and its own subnet mask-
191.203.31.87 AND 255.255.31.0
= 191.203.31.0
Since both the results are different, so host B assumes that host A is on a different network.
Thus, both can’t belong to the same network.
Hence, this option gets eliminated.
Checking Option (D)-
- Host A IP Address = 128.8.129.43
- Host B IP Address = 128.8.161.55
At Host A-
Host A computes its network address using its own IP Address and subnet mask-
128.8.129.43 AND 255.255.31.0
= 128.8.1.0
Host A computes the network address of Host B using IP Address of Host B and its own subnet mask-
128.8.161.55 AND 255.255.31.0
= 128.8.1.0
Since both the results are same, so host A assumes that host B is on the same network.
At Host B-
Host B computes its network address using its own IP Address and subnet mask-
128.8.161.55 AND 255.255.31.0
= 128.8.1.0
Host B computes the network address of Host A using IP Address of Host A and its own subnet mask-
128.8.129.43 AND 255.255.31.0
= 128.8.1.0
Since both the results are same, so host B assumes that host A is on the same network.
Thus, both the hosts assume that they belong to the same network.
Hence, Option (D) is correct.
To gain better understanding about Subnet Mask Use,
Next Article- Internet Protocol Version 4 | IPv4 Header
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.