Subnetting in Networking-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Subnetting.
We have discussed-
- Subnetting is a process of dividing a single network into multiple smaller networks.
- The number of sub networks created depends upon the requirement.
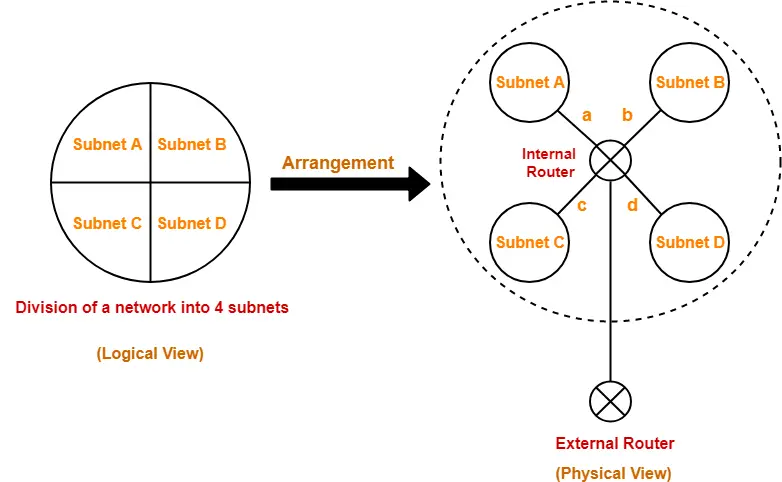
Arrangement Of Subnets-
- All the subnets are connected to an internal router.
- Internal router is connected to an external router.
- The link connecting the internal router with a subnet is called as an interface.
Example-
Working-
When a data packet arrives,
- External router forwards the data packet to the internal router.
- Internal router identifies the interface on which it should forward the incoming data packet.
- Internal router forwards the data packet on that interface.
Routing Table-
- A table is maintained by the internal router called as Routing table.
- It helps the internal router to decide on which interface the data packet should be forwarded.
Routing table consists of the following three fields-
- IP Address of the destination subnet
- Subnet mask of the subnet
- Interface
Also Read- Subnet Mask
Example-
Consider a network is subnetted into 4 subnets as shown in the above picture.
The IP Address of the 4 subnets are-
- 200.1.2.0 (Subnet A)
- 200.1.2.64 (Subnet B)
- 200.1.2.128 (Subnet C)
- 200.1.2.192 (Subnet D)
Then, Routing table maintained by the internal router looks like-
| Destination | Subnet Mask | Interface |
| 200.1.2.0 | 255.255.255.192 | a |
| 200.1.2.64 | 255.255.255.192 | b |
| 200.1.2.128 | 255.255.255.192 | c |
| 200.1.2.192 | 255.255.255.192 | d |
| Default | 0.0.0.0 | e |
Routing Table Example
When a data packet arrives to the internal router, it follows the following steps-
Step-01:
Router performs the bitwise ANDing of-
- Destination IP Address mentioned on the data packet
- And all the subnet masks one by one.
Step-02:
Router compares each result with their corresponding IP Address of the destination subnet in the routing table.
Then, following three cases may occur-
Case-01:
If there occurs only one match,
- Router forwards the data packet on the corresponding interface.
Case-02:
If there occurs more than one match,
- Router forwards the data packet on the interface corresponding to the longest subnet mask.
Case-03:
If there occurs no match,
- Router forwards the data packet on the interface corresponding to the default entry.
Important Notes-
Note-01:
In fixed length subnetting,
- All the subnets have the same subnet mask.
- So, bitwise ANDing is performed only once.
If the result matches to any of the destination subnet IP Address,
- Router forwards the data packet on its corresponding interface.
- Otherwise, it is forwarded on the default interface.
Note-02:
In variable length subnetting,
- All the subnets do not have the same subnet mask.
- So, bitwise ANDing is performed once with each subnet mask.
- Then, the above three cases are followed.
Note-03:
- A host may also be directly connected to the router.
- In that case, there exists a host specific route from the router to the host.
- Router saves the IP Address of that host in the “Destination Network” column.
- Router saves 255.255.255.255 in the “Subnet Mask” column.
- The ANDing of its destination address and subnet mask yields the IP Address of the host.
- When a data packet arrives for that specific host, bitwise ANDing is performed.
- When the result of ANDing is the IP Address of the host, packet is forwarded to its host specific route.
Note-04:
- Subnet mask for default route = 0.0.0.0
- Subnet mask for host specific route = 255.255.255.255
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON ROUTING TABLE-
Problem-01:
A router uses the following routing table-
| Destination | Mask | Interface |
| 144.16.0.0 | 255.255.0.0 | eth0 |
| 144.16.64.0 | 255.255.224.0 | eth1 |
| 144.16.68.0 | 255.255.255.0 | eth2 |
| 144.16.68.64 | 255.255.255.224 | eth3 |
A packet bearing a destination address 144.16.68.117 arrives at the router. On which interface will it be forwarded?
- eth0
- eth1
- eth2
- eth3
Solution-
Router performs the bitwise ANDing of-
- Destination address mentioned on the data packet
- And each subnet mask one by one.
1st Row-
144.16.68.117 AND 255.255.0.0
= 144.16.0.0
Since result is same as the given destination address, so a match occurs.
2nd Row-
144.16.68.117 AND 255.255.224.0
= 144.16.64.0
Since result is same as the given destination address, so a match occurs.
3rd Row-
144.16.68.117 AND 255.255.255.0
= 144.16.68.0
Since result is same as the given destination address, so a match occurs.
4th Row-
144.16.68.117 AND 255.255.255.224
= 144.16.68.96
Since result is not same as the given destination address, so a match does not occur.
Now,
- Clearly, there occurs more than one match.
- So, router forwards the packet on the interface corresponding to the longest subnet mask.
- Out of all, 255.255.255.0 is the longest subnet mask since it has maximum number of 1s.
So,
- Router forwards the packet on the interface corresponding to the subnet mask 255.255.255.0.
- The corresponding interface is eth2.
Thus, Option (C) is correct.
Problem-02:
The routing table of a router is shown below-
| Destination | Mask | Interface |
| 128.75.43.0 | 255.255.255.0 | eth0 |
| 128.75.43.0 | 255.255.255.128 | eth1 |
| 192.12.17.5 | 255.255.255.255 | eth3 |
| default | eth2 |
On which interfaces will the router forward packets addressed to destination 128.75.43.16 and 192.12.17.10 respectively?
- eth1 and eth2
- eth0 and eth2
- eth0 and eth3
- eth1 and eth3
Solution-
Router performs the bitwise ANDing of-
- Destination address mentioned on the data packet
- And each subnet mask one by one.
Packet With Destination Address 128.75.43.16-
1st Row-
128.75.43.16 AND 255.255.255.0
= 128.75.43.0
Since result is same as the given destination address, so a match occurs.
2nd Row-
128.75.43.16 AND 255.255.255.128
= 128.75.43.0
Since result is same as the given destination address, so a match occurs.
3rd Row-
128.75.43.16 AND 255.255.255.255
= 128.75.43.16
Since result is not same as the given destination address, so a match does not occur.
Now,
- Clearly, there occurs more than one match.
- So, router forwards the packet on the interface corresponding to the longest subnet mask.
- Out of all, 255.255.255.128 is the longest subnet mask since it has maximum number of 1s.
So,
- Router forwards the packet on the interface corresponding to the subnet mask 255.255.255.128.
- The corresponding interface is eth1.
Packet With Destination Address 192.12.17.10-
1st Row-
192.12.17.10 AND 255.255.255.0
= 192.12.17.0
Since result is not same as the given destination address, so a match does not occur.
2nd Row-
192.12.17.10 AND 255.255.255.128
= 192.12.17.0
Since result is not same as the given destination address, so a match does not occur.
3rd Row-
192.12.17.10 AND 255.255.255.255
= 192.12.17.10
Since result is not same as the given destination address, so a match does not occur.
Now,
- Clearly, there occurs no match.
- So, router forwards the packet on the interface corresponding to the default entry.
- The corresponding interface is eth2.
Thus, Option (A) is correct.
Problem-03:
Host specific route has a subnet mask of _____ in the routing table.
- 255.255.255.255
- 0.0.0.0
- 255.0.0.0
- 0.0.0.255
Solution-
Option (A) is correct.
Problem-04:
Default route has a subnet mask of _____ in the routing table.
- 255.255.255.255
- 0.0.0.0
- 255.0.0.0
- 0.0.0.255
Solution-
Option (B) is correct.
Problem-05:
Default route can be described as-
- Destination values of 0.0.0.0 in the routing table
- It can be used if network has only one next hop router
- It is useful in keeping routing table small
- All of the above
Solution-
Option (D) is correct.
To gain better understanding about Routing Table,
Next Article- Use of Subnet Mask
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

