Switching in Computer Networks-
| The process of moving the data packets towards their destination by forwarding them from one port to the other port is called as switching. |
Switching Techniques-
Various switching techniques are-
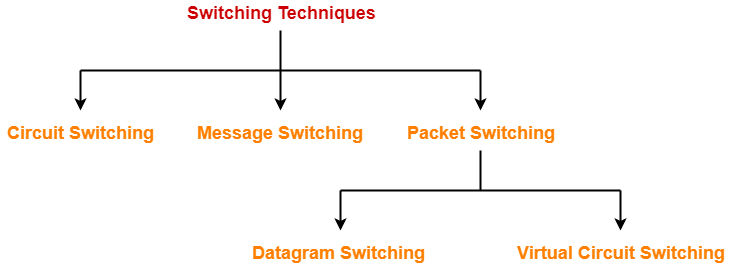
In this article, we will perform a comparison between circuit switching and packet switching.
Difference Between Circuit Switching And Packet Switching-
The following table compares circuit switching and packet switching techniques-
| Circuit Switching | Packet Switching | |
| Virtual Circuit Switching | Datagram Switching | |
| Connection oriented service | Connection oriented service | Connection less service |
| Ensures in order delivery | Ensures in order delivery | Packets may be delivered out of order |
| No reordering is required | No reordering is required | Reordering is required |
| A dedicated path exists for data transfer | A dedicated path exists for data transfer | No dedicated path exists for data transfer |
| All the packets take the same path | All the packets take the same path | All the packets may not take the same path |
| Resources are allocated before data transfer | Resources are allocated on demand using 1st packet | No resources are allocated |
| Stream oriented | Packet oriented | Packet oriented |
| Fixed bandwidth | Dynamic Bandwidth | Dynamic bandwidth |
| Reliable | Reliable | Unreliable |
| No header overheads | Only label overheads | Higher overheads |
| Implemented at physical layer | Implemented at data link layer | Implemented at network layer |
| Inefficient in terms of resource utilization | Provides better efficiency than circuit switched systems | Provides better efficiency than message switched systems |
| Example- Telephone systems | Examples- X.25, Frame relay | Example- Internet |
To gain better understanding about Circuit Switching Vs Packet Switching,
Next Article- Distance Vector Routing | Routing Algorithms
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.