CPU Scheduling Algorithms-
Various CPU scheduling algorithms are-
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON CPU SCHEDULING ALGORITHMS-
Problem-01:
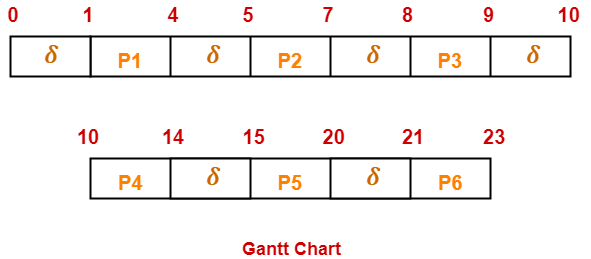
Consider three process, all arriving at time zero, with total execution time of 10, 20 and 30 units respectively. Each process spends the first 20% of execution time doing I/O, the next 70% of time doing computation, and the last 10% of time doing I/O again. The operating system uses a shortest remaining compute time first scheduling algorithm and schedules a new process either when the running process gets blocked on I/O or when the running process finishes its compute burst. Assume that all I/O operations can be overlapped as much as possible. For what percentage of does the CPU remain idle?
- 0%
- 10.6%
- 30.0%
- 89.4%
Solution-
According to question, we have-
| Total Burst Time | I/O Burst | CPU Burst | I/O Burst | |
| Process P1 | 10 | 2 | 7 | 1 |
| Process P2 | 20 | 4 | 14 | 2 |
| Process P3 | 30 | 6 | 21 | 3 |
The scheduling algorithm used is Shortest Remaining Time First.
Gantt Chart-
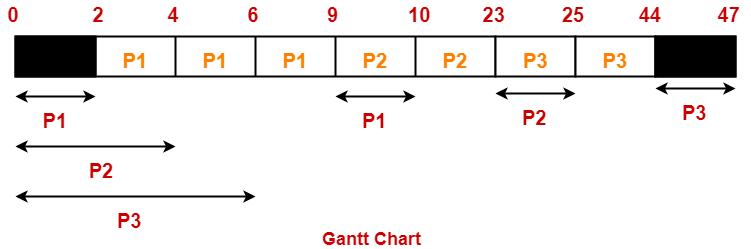
Percentage of time CPU remains idle
= (5 / 47) x 100
= 10.638%
Thus, Option (B) is correct.
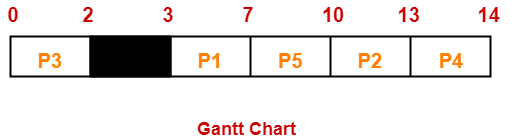
Problem-02:
Consider the set of 4 processes whose arrival time and burst time are given below-
| Process No. | Arrival Time | Burst Time | ||
| CPU Burst | I/O Burst | CPU Burst | ||
| P1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| P2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| P3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| P4 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
If the CPU scheduling policy is Shortest Remaining Time First, calculate the average waiting time and average turn around time.
Solution-
Gantt Chart-
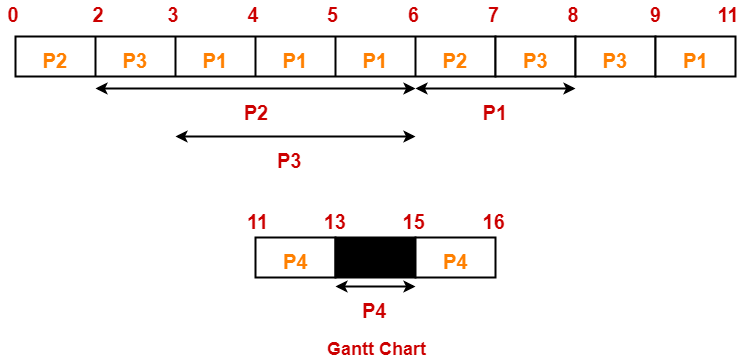
Now, we know-
- Turn Around time = Exit time – Arrival time
- Waiting time = Turn Around time – Burst time
Also read- Various Times Of Process
| Process Id | Exit time | Turn Around time | Waiting time |
| P1 | 11 | 11 – 0 = 11 | 11 – (3+2) = 6 |
| P2 | 7 | 7 – 0 = 7 | 7 – (2+1) = 4 |
| P3 | 9 | 9 – 2 = 7 | 7 – (1+2) = 4 |
| P4 | 16 | 16 – 5 = 11 | 11 – (2+1) = 8 |
Now,
- Average Turn Around time = (11 + 7 + 7 + 11) / 4 = 36 / 4 = 9 units
- Average waiting time = (6 + 4 + 4 + 8) / 4 = 22 / 5 = 4.4 units
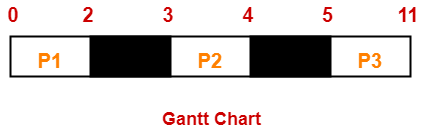
Problem-03:
Consider the set of 4 processes whose arrival time and burst time are given below-
| Process No. | Arrival Time | Priority | Burst Time | ||
| CPU Burst | I/O Burst | CPU Burst | |||
| P1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 3 |
| P2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| P3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
If the CPU scheduling policy is Priority Scheduling, calculate the average waiting time and average turn around time. (Lower number means higher priority)
Solution-
The scheduling algorithm used is Priority Scheduling.
Gantt Chart-
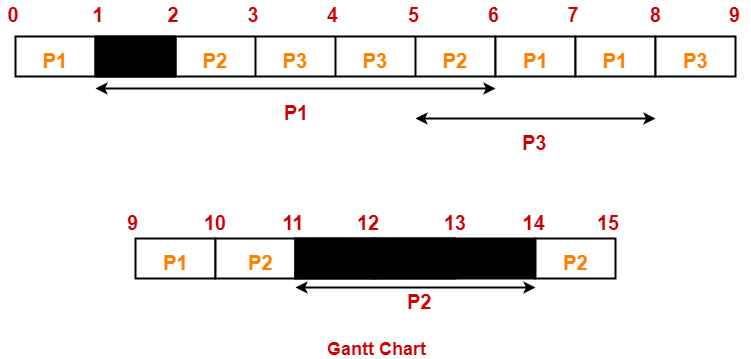
Now, we know-
- Turn Around time = Exit time – Arrival time
- Waiting time = Turn Around time – Burst time
| Process Id | Exit time | Turn Around time | Waiting time |
| P1 | 10 | 10 – 0 = 10 | 10 – (1+3) = 6 |
| P2 | 15 | 15 – 2 = 13 | 13 – (3+1) = 9 |
| P3 | 9 | 9 – 3 = 6 | 6 – (2+1) = 3 |
Now,
- Average Turn Around time = (10 + 13 + 6) / 3 = 29 / 3 = 9.67 units
- Average waiting time = (6 + 9 + 3) / 3 = 18 / 3 = 6 units
Next Article- Introduction to Process Synchronization
Get more notes and other study material of Operating System.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.