Disk Scheduling-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Magnetic Disk.
| Disk scheduling is a technique used by the operating system to schedule multiple requests for accessing the disk. |
Disk Scheduling Algorithms-
- The algorithms used for disk scheduling are called as disk scheduling algorithms.
- The purpose of disk scheduling algorithms is to reduce the total seek time.
Various disk scheduling algorithms are-
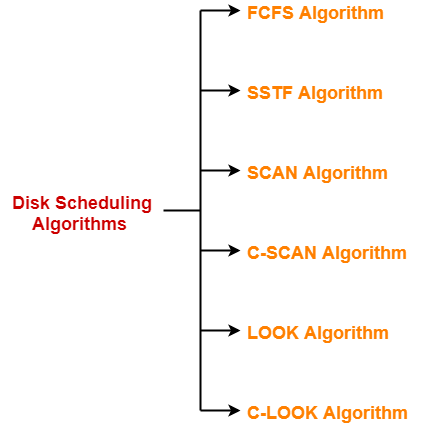
- FCFS Algorithm
- SSTF Algorithm
- SCAN Algorithm
- C-SCAN Algorithm
- LOOK Algorithm
- C-LOOK Algorithm
In this article, we will discuss about FCFS Disk Scheduling Algorithm.
FCFS Disk Scheduling Algorithm-
- As the name suggests, this algorithm entertains requests in the order they arrive in the disk queue.
- It is the simplest disk scheduling algorithm.
Advantages-
- It is simple, easy to understand and implement.
- It does not cause starvation to any request.
Disadvantages-
- It results in increased total seek time.
- It is inefficient.
PRACTICE PROBLEM BASED ON FCFS DISK SCHEDULING ALGORITHM-
Problem-
Consider a disk queue with requests for I/O to blocks on cylinders 98, 183, 41, 122, 14, 124, 65, 67. The FCFS scheduling algorithm is used. The head is initially at cylinder number 53. The cylinders are numbered from 0 to 199. The total head movement (in number of cylinders) incurred while servicing these requests is _______.
Solution-
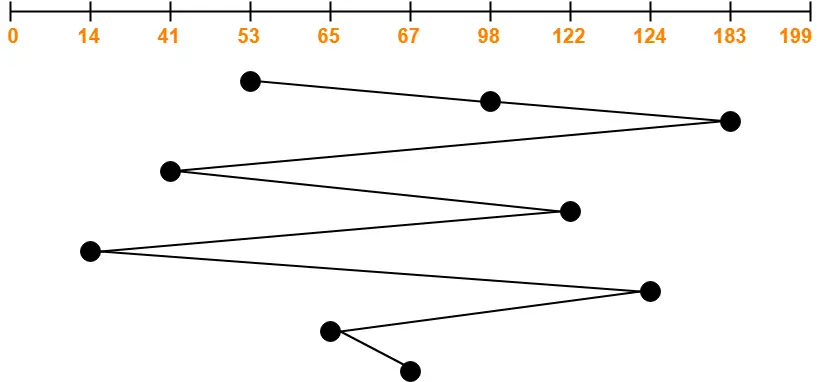
Total head movements incurred while servicing these requests
= (98 – 53) + (183 – 98) + (183 – 41) + (122 – 41) + (122 – 14) + (124 – 14) + (124 – 65) + (67 – 65)
= 45 + 85 + 142 + 81 + 108 + 110 + 59 + 2
= 632
To gain better understanding about FCFS Disk Scheduling Algorithm,
Next Article- SSTF Disk Scheduling Algorithm
Get more notes and other study material of Operating System.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.