Relational Algebra Operators-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Introduction to Relational Algebra.
The operators in relational algebra are classified as-
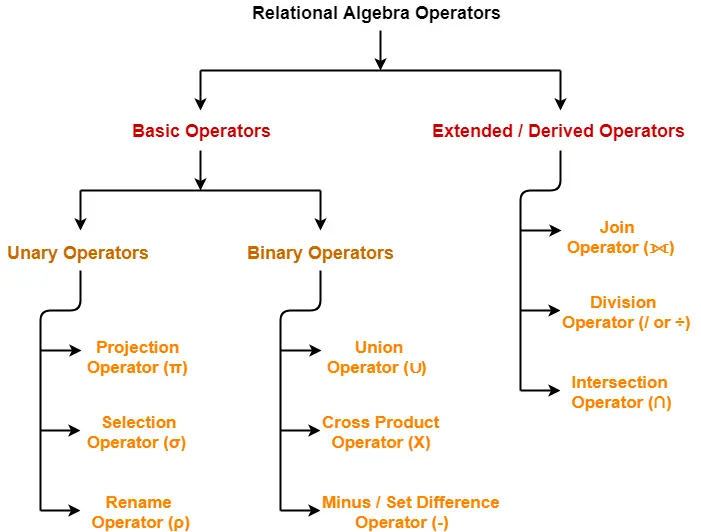
In this article, we will discuss about Set Theory Operators.
Set Theory Operators-
Following operators are called as set theory operators-
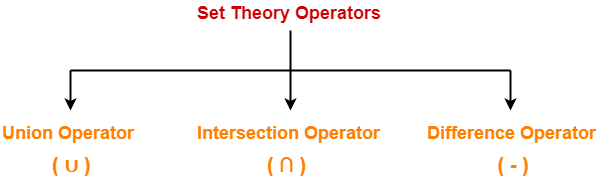
- Union Operator (∪)
- Intersection Operator (∩)
- Difference Operator (-)
Condition For Using Set Theory Operators
To use set theory operators on two relations, The two relations must be union compatible. Union compatible property means-
|
Also read- Selection Operator and Projection Operator
1. Union Operator (∪)-
Let R and S be two relations.
Then-
- R ∪ S is the set of all tuples belonging to either R or S or both.
- In R ∪ S, duplicates are automatically removed.
- Union operation is both commutative and associative.
Example-
Consider the following two relations R and S-
| ID | Name | Subject |
| 100 | Ankit | English |
| 200 | Pooja | Maths |
| 300 | Komal | Science |
Relation R
| ID | Name | Subject |
| 100 | Ankit | English |
| 400 | Kajol | French |
Relation S
Then, R ∪ S is-
| ID | Name | Subject |
| 100 | Ankit | English |
| 200 | Pooja | Maths |
| 300 | Komal | Science |
| 400 | Kajol | French |
Relation R ∪ S
2. Intersection Operator (∩)-
Let R and S be two relations.
Then-
- R ∩ S is the set of all tuples belonging to both R and S.
- In R ∩ S, duplicates are automatically removed.
- Intersection operation is both commutative and associative.
Example-
Consider the following two relations R and S-
| ID | Name | Subject |
| 100 | Ankit | English |
| 200 | Pooja | Maths |
| 300 | Komal | Science |
Relation R
| ID | Name | Subject |
| 100 | Ankit | English |
| 400 | Kajol | French |
Relation S
Then, R ∩ S is-
| ID | Name | Subject |
| 100 | Ankit | English |
Relation R ∩ S
3. Difference Operator (-)-
Let R and S be two relations.
Then-
- R – S is the set of all tuples belonging to R and not to S.
- In R – S, duplicates are automatically removed.
- Difference operation is associative but not commutative.
Example-
Consider the following two relations R and S-
| ID | Name | Subject |
| 100 | Ankit | English |
| 200 | Pooja | Maths |
| 300 | Komal | Science |
Relation R
| ID | Name | Subject |
| 100 | Ankit | English |
| 400 | Kajol | French |
Relation S
Then, R – S is-
| ID | Name | Subject |
| 200 | Pooja | Maths |
| 300 | Komal | Science |
Relation R – S
Get more notes and other study material of Database Management System (DBMS).
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.