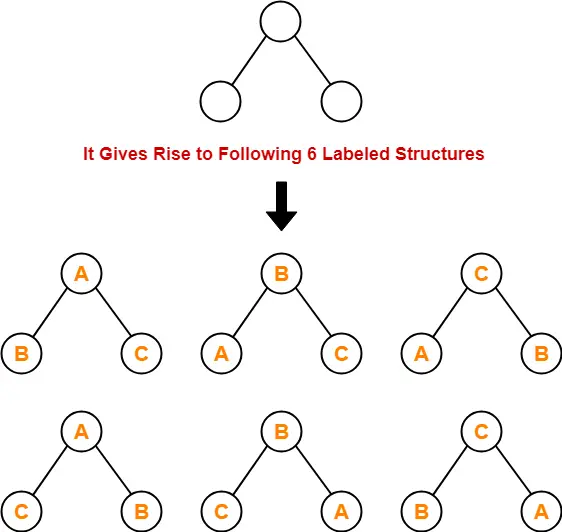
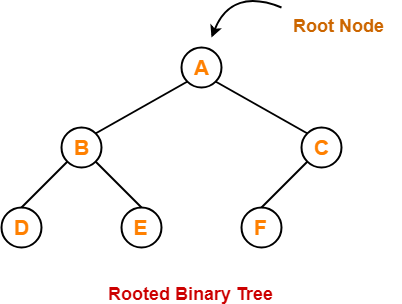
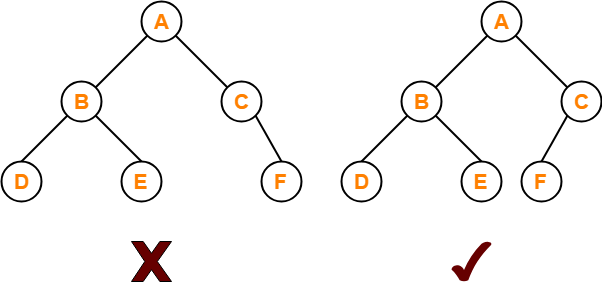
Binary Tree-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you gone through the previous article on Binary Trees.
We have discussed-
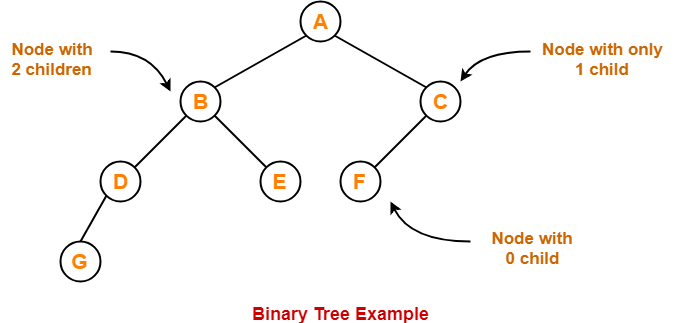
- Binary tree is a special tree data structure.
- In a binary tree, each node can have at most 2 children.
In this article, we will discuss about Binary Tree Traversal.
Tree Traversal-
| Tree Traversal refers to the process of visiting each node in a tree data structure exactly once. |
Various tree traversal techniques are-
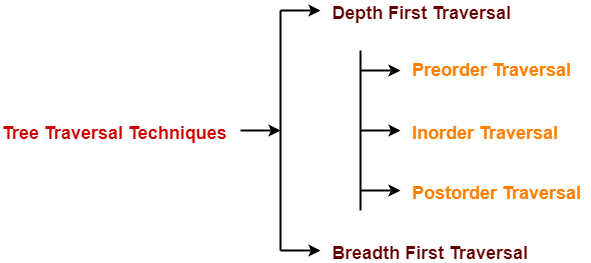
Depth First Traversal-
Following three traversal techniques fall under Depth First Traversal-
- Preorder Traversal
- Inorder Traversal
- Postorder Traversal
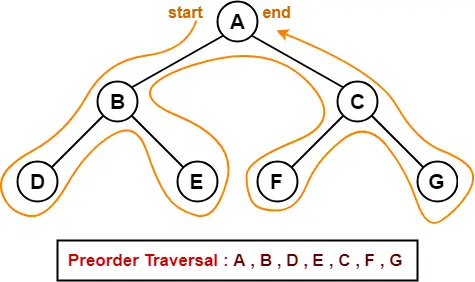
1. Preorder Traversal-
Algorithm-
- Visit the root
- Traverse the left sub tree i.e. call Preorder (left sub tree)
- Traverse the right sub tree i.e. call Preorder (right sub tree)
Root → Left → Right
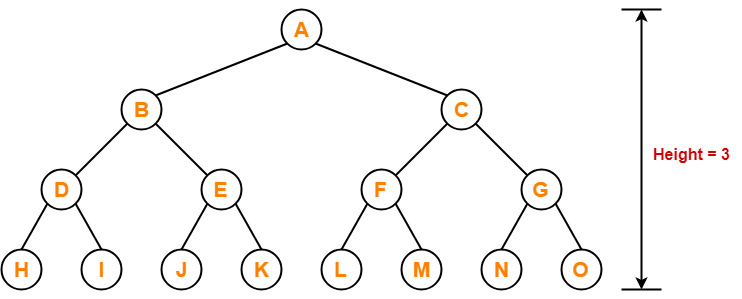
Example-
Consider the following example-
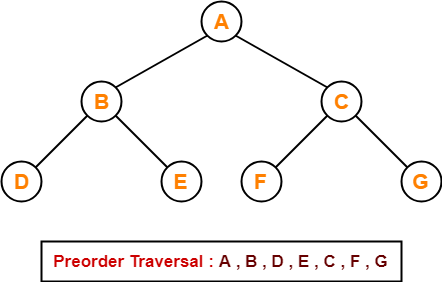
Preorder Traversal Shortcut
Traverse the entire tree starting from the root node keeping yourself to the left.
|
Applications-
- Preorder traversal is used to get prefix expression of an expression tree.
- Preorder traversal is used to create a copy of the tree.
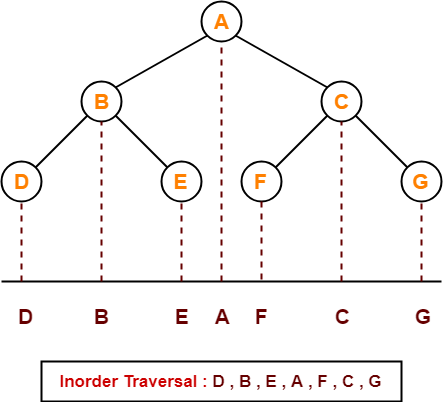
2. Inorder Traversal-
Algorithm-
- Traverse the left sub tree i.e. call Inorder (left sub tree)
- Visit the root
- Traverse the right sub tree i.e. call Inorder (right sub tree)
Left → Root → Right
Example-
Consider the following example-
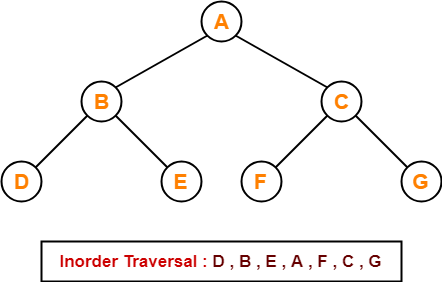
Inorder Traversal Shortcut
Keep a plane mirror horizontally at the bottom of the tree and take the projection of all the nodes.
|
Application-
- Inorder traversal is used to get infix expression of an expression tree.
3. Postorder Traversal-
Algorithm-
- Traverse the left sub tree i.e. call Postorder (left sub tree)
- Traverse the right sub tree i.e. call Postorder (right sub tree)
- Visit the root
Left → Right → Root
Example-
Consider the following example-
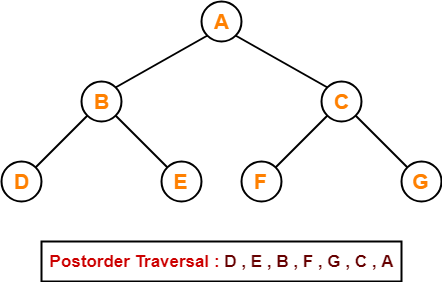
Postorder Traversal Shortcut
Pluck all the leftmost leaf nodes one by one.
|
Applications-
- Postorder traversal is used to get postfix expression of an expression tree.
- Postorder traversal is used to delete the tree.
- This is because it deletes the children first and then it deletes the parent.
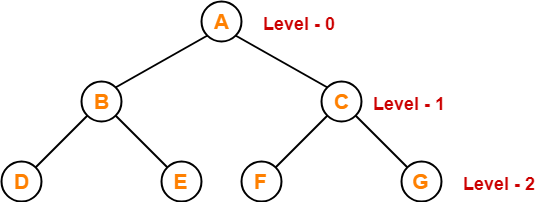
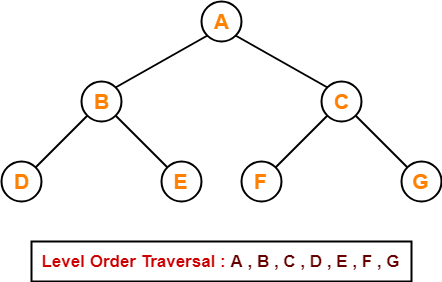
Breadth First Traversal-
- Breadth First Traversal of a tree prints all the nodes of a tree level by level.
- Breadth First Traversal is also called as Level Order Traversal.
Example-
Application-
- Level order traversal is used to print the data in the same order as stored in the array representation of a complete binary tree.
To gain better understanding about Tree Traversal,
Also Read- Binary Tree Properties
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON TREE TRAVERSAL-
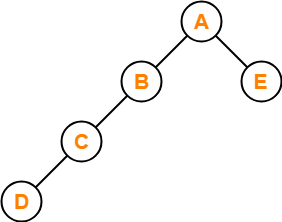
Problem-01:
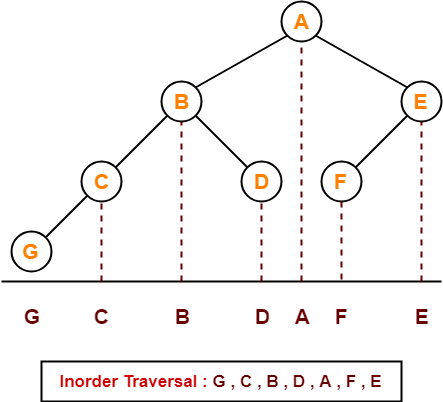
If the binary tree in figure is traversed in inorder, then the order in which the nodes will be visited is ____?
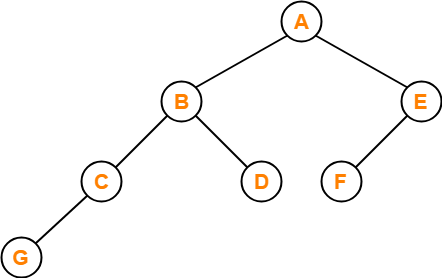
Solution-
The inorder traversal will be performed as-
Problem-02:
Which of the following sequences denotes the postorder traversal sequence of the tree shown in figure?
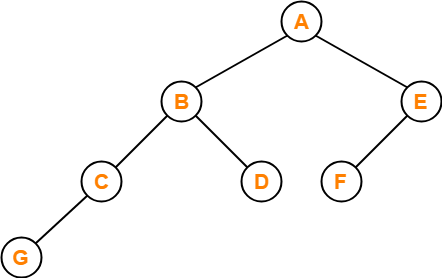
- FEGCBDBA
- GCBDAFE
- GCDBFEA
- FDEGCBA
Solution-
Perform the postorder traversal by plucking all the leftmost leaf nodes one by one.
Then,
Postorder Traversal : G , C , D , B , F , E , A
Thus, Option (C) is correct.
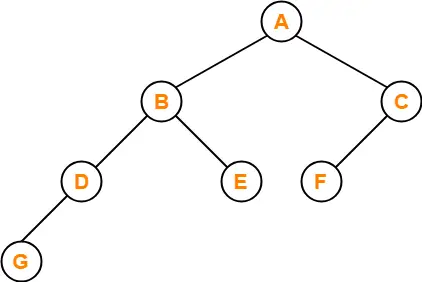
Problem-03:
Let LASTPOST, LASTIN, LASTPRE denote the last vertex visited in a postorder, inorder and preorder traversal respectively of a complete binary tree. Which of the following is always true?
- LASTIN = LASTPOST
- LASTIN = LASTPRE
- LASTPRE = LASTPOST
- None of these
Solution-
Consider the following complete binary tree-
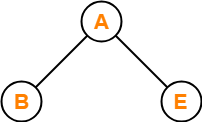
Preorder Traversal : B , A , E
Inorder Traversal : B , A , E
Postorder Traversal : B , E , A
Clearly, LASTIN = LASTPRE.
Thus, Option (B) is correct.
Problem-04:
Which of the following binary trees has its inorder and preorder traversals as BCAD and ABCD respectively-
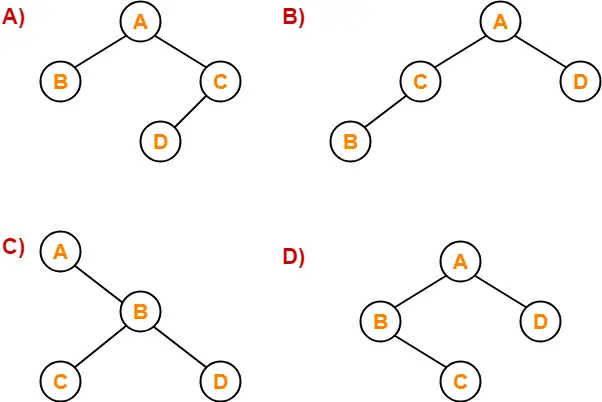
Solution-
Option (D) is correct.
To watch video solutions and practice more problems,
Download Handwritten Notes Here-
Next Article- Binary Search Trees
Get more notes and other study material of Data Structures.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.