Circle Drawing Algorithms-
In computer graphics, popular algorithms used to generate circle are-

- Mid Point Circle Drawing Algorithm
- Bresenham Circle Drawing Algorithm
In this article, we will discuss about Bresenham Circle Drawing Algorithm.
Bresenham Circle Drawing Algorithm-
| Given the centre point and radius of circle,
Bresenham Circle Drawing Algorithm attempts to generate the points of one octant. |
The points for other octacts are generated using the eight symmetry property.
Also Read- Mid Point Circle Drawing Algorithm
Procedure-
Given-
- Centre point of Circle = (X0, Y0)
- Radius of Circle = R
The points generation using Bresenham Circle Drawing Algorithm involves the following steps-
Step-01:
Assign the starting point coordinates (X0, Y0) as-
- X0 = 0
- Y0 = R
Step-02:
Calculate the value of initial decision parameter P0 as-
P0 = 3 – 2 x R
Step-03:
Suppose the current point is (Xk, Yk) and the next point is (Xk+1, Yk+1).
Find the next point of the first octant depending on the value of decision parameter Pk.
Follow the below two cases-
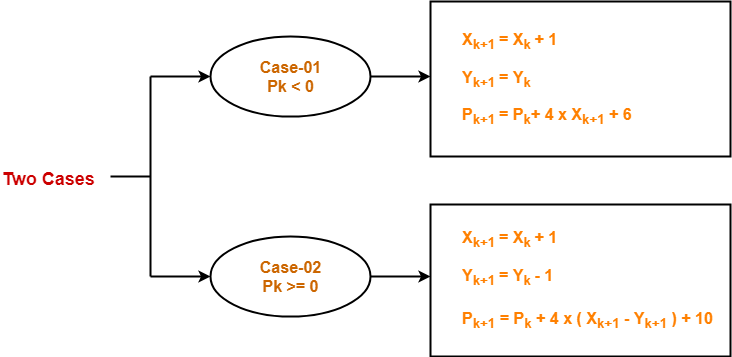
Step-04:
If the given centre point (X0, Y0) is not (0, 0), then do the following and plot the point-
- Xplot = Xc + X0
- Yplot = Yc + Y0
Here, (Xc, Yc) denotes the current value of X and Y coordinates.
Step-05:
Keep repeating Step-03 and Step-04 until Xplot => Yplot.
Step-06:
Step-05 generates all the points for one octant.
To find the points for other seven octants, follow the eight symmetry property of circle.
This is depicted by the following figure-
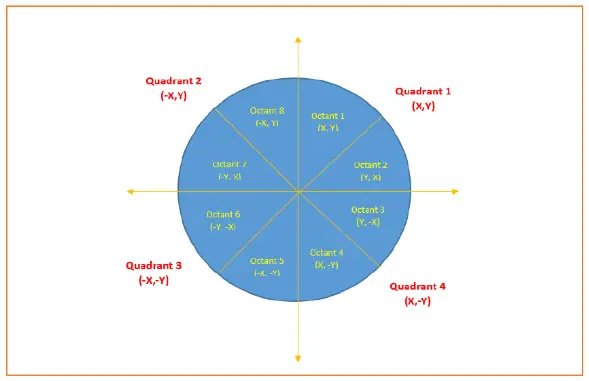
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON BRESENHAM CIRCLE DRAWING ALGORITHM-
Problem-01:
Given the centre point coordinates (0, 0) and radius as 8, generate all the points to form a circle.
Solution-
Given-
- Centre Coordinates of Circle (X0, Y0) = (0, 0)
- Radius of Circle = 8
Step-01:
Assign the starting point coordinates (X0, Y0) as-
- X0 = 0
- Y0 = R = 8
Step-02:
Calculate the value of initial decision parameter P0 as-
P0 = 3 – 2 x R
P0 = 3 – 2 x 8
P0 = -13
Step-03:
As Pinitial < 0, so case-01 is satisfied.
Thus,
- Xk+1 = Xk + 1 = 0 + 1 = 1
- Yk+1 = Yk = 8
- Pk+1 = Pk + 4 x Xk+1 + 6 = -13 + (4 x 1) + 6 = -3
Step-04:
This step is not applicable here as the given centre point coordinates is (0, 0).
Step-05:
Step-03 is executed similarly until Xk+1 >= Yk+1 as follows-
| Pk | Pk+1 | (Xk+1, Yk+1) |
| (0, 8) | ||
| -13 | -3 | (1, 8) |
| -3 | 11 | (2, 8) |
| 11 | 5 | (3, 7) |
| 5 | 7 | (4, 6) |
| 7 | (5, 5) | |
|
Algorithm Terminates
These are all points for Octant-1. |
||
Algorithm calculates all the points of octant-1 and terminates.
Now, the points of octant-2 are obtained using the mirror effect by swapping X and Y coordinates.
| Octant-1 Points | Octant-2 Points |
| (0, 8) | (5, 5) |
| (1, 8) | (6, 4) |
| (2, 8) | (7, 3) |
| (3, 7) | (8, 2) |
| (4, 6) | (8, 1) |
| (5, 5) | (8, 0) |
| These are all points for Quadrant-1. | |
Now, the points for rest of the part are generated by following the signs of other quadrants.
The other points can also be generated by calculating each octant separately.
Here, all the points have been generated with respect to quadrant-1-
| Quadrant-1 (X,Y) | Quadrant-2 (-X,Y) | Quadrant-3 (-X,-Y) | Quadrant-4 (X,-Y) |
| (0, 8) | (0, 8) | (0, -8) | (0, -8) |
| (1, 8) | (-1, 8) | (-1, -8) | (1, -8) |
| (2, 8) | (-2, 8) | (-2, -8) | (2, -8) |
| (3, 7) | (-3, 7) | (-3, -7) | (3, -7) |
| (4, 6) | (-4, 6) | (-4, -6) | (4, -6) |
| (5, 5) | (-5, 5) | (-5, -5) | (5, -5) |
| (6, 4) | (-6, 4) | (-6, -4) | (6, -4) |
| (7, 3) | (-7, 3) | (-7, -3) | (7, -3) |
| (8, 2) | (-8, 2) | (-8, -2) | (8, -2) |
| (8, 1) | (-8, 1) | (-8, -1) | (8, -1) |
| (8, 0) | (-8, 0) | (-8, 0) | (8, 0) |
|
These are all points of the Circle. |
|||
Problem-02:
Given the centre point coordinates (10, 10) and radius as 10, generate all the points to form a circle.
Solution-
Given-
- Centre Coordinates of Circle (X0, Y0) = (10, 10)
- Radius of Circle = 10
Step-01:
Assign the starting point coordinates (X0, Y0) as-
- X0 = 0
- Y0 = R = 10
Step-02:
Calculate the value of initial decision parameter P0 as-
P0 = 3 – 2 x R
P0 = 3 – 2 x 10
P0 = -17
Step-03:
As Pinitial < 0, so case-01 is satisfied.
Thus,
- Xk+1 = Xk + 1 = 0 + 1 = 1
- Yk+1 = Yk = 10
- Pk+1 = Pk + 4 x Xk+1 + 6 = -17 + (4 x 1) + 6 = -7
Step-04:
This step is applicable here as the given centre point coordinates is (10, 10).
Xplot = Xc + X0 = 1 + 10 = 11
Yplot = Yc + Y0 = 10 + 10 = 20
Step-05:
Step-03 and Step-04 are executed similarly until Xplot => Yplot as follows-
| Pk | Pk+1 | (Xk+1, Yk+1) | (Xplot, Yplot) |
| (0, 10) | (10, 20) | ||
| -17 | -7 | (1, 10) | (11, 20) |
| -7 | 7 | (2, 10) | (12, 20) |
| 7 | -7 | (3, 9) | (13, 19) |
| -7 | 15 | (4, 9) | (14, 19) |
| 15 | 13 | (5, 8) | (15, 18) |
| 13 | 19 | (6, 7) | (16, 17) |
|
Algorithm Terminates
These are all points for Octant-1. |
|||
Algorithm calculates all the points of octant-1 and terminates.
Now, the points of octant-2 are obtained using the mirror effect by swapping X and Y coordinates.
| Octant-1 Points | Octant-2 Points |
| (10, 20) | (17, 16) |
| (11, 20) | (18, 15) |
| (12, 20) | (19, 14) |
| (13, 19) | (19, 13) |
| (14, 19) | (20, 12) |
| (15, 18) | (20, 11) |
| (16, 17) | (20, 10) |
| These are all points for Quadrant-1. | |
Now, the points for rest of the part are generated by following the signs of other quadrants.
The other points can also be generated by calculating each octant separately.
Here, all the points have been generated with respect to quadrant-1-
| Quadrant-1 (X,Y) | Quadrant-2 (-X,Y) | Quadrant-3 (-X,-Y) | Quadrant-4 (X,-Y) |
| (10, 20) | (10, 20) | (10, 0) | (10, 0) |
| (11, 20) | (9, 20) | (9, 0) | (11, 0) |
| (12, 20) | (8, 20) | (8, 0) | (12, 0) |
| (13, 19) | (7, 19) | (7, 1) | (13, 1) |
| (14, 19) | (6, 19) | (6, 1) | (14, 1) |
| (15, 18) | (5, 18) | (5, 2) | (15, 2) |
| (16, 17) | (4, 17) | (4, 3) | (16, 3) |
| (17, 16) | (3, 16) | (3, 4) | (17, 4) |
| (18, 15) | (2, 15) | (2, 5) | (18, 5) |
| (19, 14) | (1, 14) | (1, 6) | (19, 6) |
| (19, 13) | (1, 13) | (1, 7) | (19, 7) |
| (20, 12) | (0, 12) | (0, 8) | (20, 8) |
| (20, 11) | (0, 11) | (0, 9) | (20, 9) |
| (20, 10) | (0, 10) | (0, 10) | (20, 10) |
|
These are all points of the Circle. |
|||
Advantages of Bresenham Circle Drawing Algorithm-
The advantages of Bresenham Circle Drawing Algorithm are-
- The entire algorithm is based on the simple equation of circle X2 + Y2 = R2.
- It is easy to implement.
Disadvantages of Bresenham Circle Drawing Algorithm-
The disadvantages of Bresenham Circle Drawing Algorithm are-
- Like Mid Point Algorithm, accuracy of the generating points is an issue in this algorithm.
- This algorithm suffers when used to generate complex and high graphical images.
- There is no significant enhancement with respect to performance.
To gain better understanding about Bresenham Circle Drawing Algorithm,
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Graphics.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

