Cache Mapping-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Cache Mapping.
| Cache mapping is a technique by which the contents of main memory are brought into the cache memory. |
Different cache mapping techniques are-
- Direct Mapping
- Fully Associative Mapping
- K-way Set Associative Mapping
In this article, we will discuss about set associative mapping in detail.
Set Associative Mapping-
In k-way set associative mapping,
- Cache lines are grouped into sets where each set contains k number of lines.
- A particular block of main memory can map to only one particular set of the cache.
- However, within that set, the memory block can map to any freely available cache line.
- The set of the cache to which a particular block of the main memory can map is given by-
|
Cache set number
= ( Main Memory Block Address ) Modulo (Number of sets in Cache) |
Division of Physical Address-
In set associative mapping, the physical address is divided as-

Set Associative Cache-
| Set associative cache employs set associative cache mapping technique. |
The following steps explain the working of set associative cache-
After CPU generates a memory request,
- The set number field of the address is used to access the particular set of the cache.
- The tag field of the CPU address is then compared with the tags of all k lines within that set.
- If the CPU tag matches to the tag of any cache line, a cache hit occurs.
- If the CPU tag does not match to the tag of any cache line, a cache miss occurs.
- In case of a cache miss, the required word has to be brought from the main memory.
- If the cache is full, a replacement is made in accordance with the employed replacement policy.
Implementation-
The following diagram shows the implementation of 2-way set associative cache-
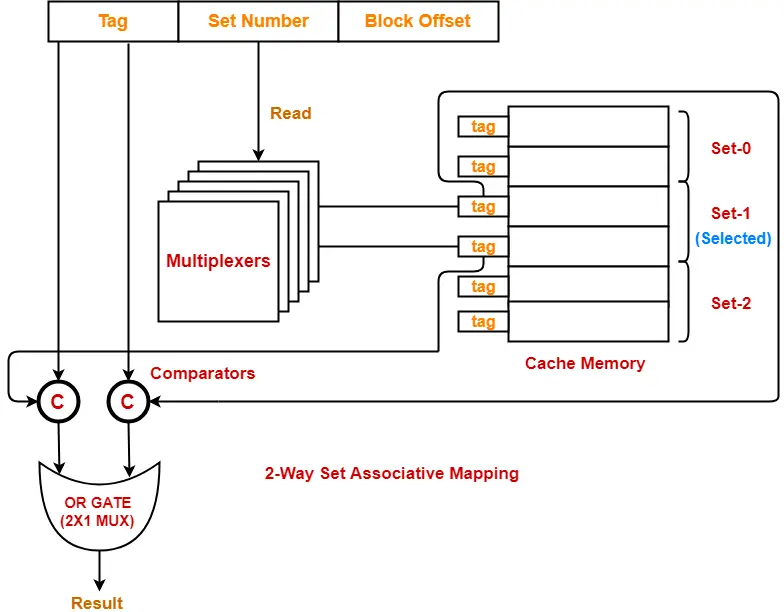
(For simplicity, this diagram shows does not show all the lines of multiplexers)
The steps involved are as follows-
Step-01:
- Each multiplexer reads the set number from the generated physical address using its select lines in parallel.
- To read the set number of S bits, number of select lines each multiplexer must have = S.
Step-02:
- After reading the set number, each multiplexer goes to the corresponding set in the cache memory.
- Then, each multiplexer goes to the lines of that set using its input lines in parallel.
- Number of input lines each multiplexer must have = Number of lines in one set
Step-03:
- Each multiplexer outputs the tag bit it has selected from the lines of selected set to the comparators using its output line.
- Number of output line in each multiplexer = 1.
UNDERSTAND
It is important to understand-
Number of multiplexers required = Number of bits in the tag
Number of multiplexers required = Number of lines in one set (k) x Number of bits in the tag
|
Step-04:
- Comparators compare the tags coming from the multiplexers with the tag of the generated address.
- This comparison takes place in parallel.
- If there are k lines in one set (thus k tags), then-
Number of comparators required = k
and
Size of each comparator = Number of bits in the tag
- The output result of each comparator is fed as an input to an OR Gate.
- OR Gate is usually implemented using 2 x 1 multiplexer.
- If the output of OR Gate is 1, a cache hit occurs otherwise a cache miss occurs.
Hit latency-
- The time taken to find out whether the required word is present in the Cache Memory or not is called as hit latency.
For set associative mapping,
| Hit latency = Multiplexer latency + Comparator latency + OR Gate latency |
Also Read- Direct Mapped Cache | Implementation & Formulas
Important Results-
Following are the few important results for set associative cache-
- Block j of main memory maps to set number (j mod number of sets in cache) of the cache.
- Number of multiplexers required = Number of lines in one set (k) x Number of bits in tag
- Size of each multiplexer = Number of lines in one set (k) x 1
- Number of comparators required = Number of lines in one set (k)
- Size of each comparator = Number of bits in the tag
- Hit latency = Multiplexer latency + Comparator latency + OR Gate latency
To gain better understanding about set associative mapping,
Next Article- Practice Problems On Set Associative Mapping
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Organization and Architecture.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

