Cardinality Constraint-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Introduction to ER Diagrams.
| Cardinality constraint defines the maximum number of relationship instances in which an entity can participate. |
Types of Cardinality Ratios-
There are 4 types of cardinality ratios-
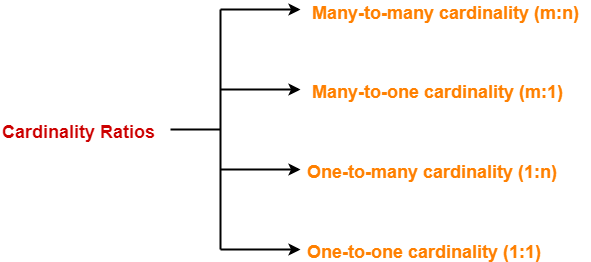
- Many-to-Many cardinality (m:n)
- Many-to-One cardinality (m:1)
- One-to-Many cardinality (1:n)
- One-to-One cardinality (1:1 )
Also read- Relationship Sets in DBMS and Entity Sets in DBMS
1. Many-to-Many Cardinality-
By this cardinality constraint,
- An entity in set A can be associated with any number (zero or more) of entities in set B.
- An entity in set B can be associated with any number (zero or more) of entities in set A.
Symbol Used-

Example-
Consider the following ER diagram-

Here,
- One student can enroll in any number (zero or more) of courses.
- One course can be enrolled by any number (zero or more) of students.
2. Many-to-One Cardinality-
By this cardinality constraint,
- An entity in set A can be associated with at most one entity in set B.
- An entity in set B can be associated with any number (zero or more) of entities in set A.
Symbol Used-

Example-
Consider the following ER diagram-
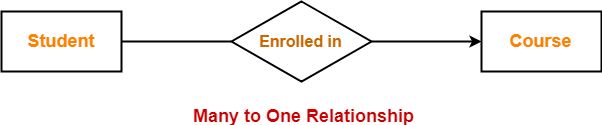
Here,
- One student can enroll in at most one course.
- One course can be enrolled by any number (zero or more) of students.
3. One-to-Many Cardinality-
By this cardinality constraint,
- An entity in set A can be associated with any number (zero or more) of entities in set B.
- An entity in set B can be associated with at most one entity in set A.
Symbol Used-

Example-
Consider the following ER diagram-
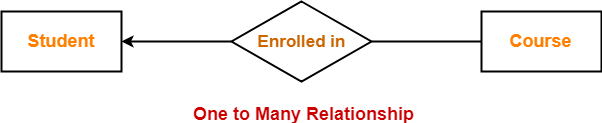
Here,
- One student can enroll in any number (zero or more) of courses.
- One course can be enrolled by at most one student.
4. One-to-One Cardinality-
By this cardinality constraint,
- An entity in set A can be associated with at most one entity in set B.
- An entity in set B can be associated with at most one entity in set A.
Symbol Used-
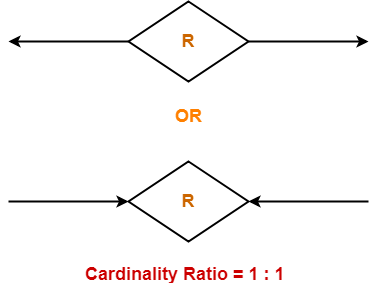
Example-
Consider the following ER diagram-

Here,
- One student can enroll in at most one course.
- One course can be enrolled by at most one student.
Next Article- Participation Constraints
Get more notes and other study material of Database Management System (DBMS).
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.
Summary

Article Name
Cardinality in ER Diagram | DBMS
DescriptionCardinality in DBMS defines the maximum number of relationship instances in which an entity can participate. Cardinality Ratios are- Many to Many Cardinality, Many to One Cardinality, One to Many Cardinality, One to One Cardinality.
Author
Akshay Singhal
Publisher Name

Gate Vidyalay
Publisher Logo
