Schedules in DBMS-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Transactions in DBMS.
| The order in which the operations of multiple transactions appear for execution is called as a schedule. |
Types of Schedules-
In DBMS, schedules may be classified as-
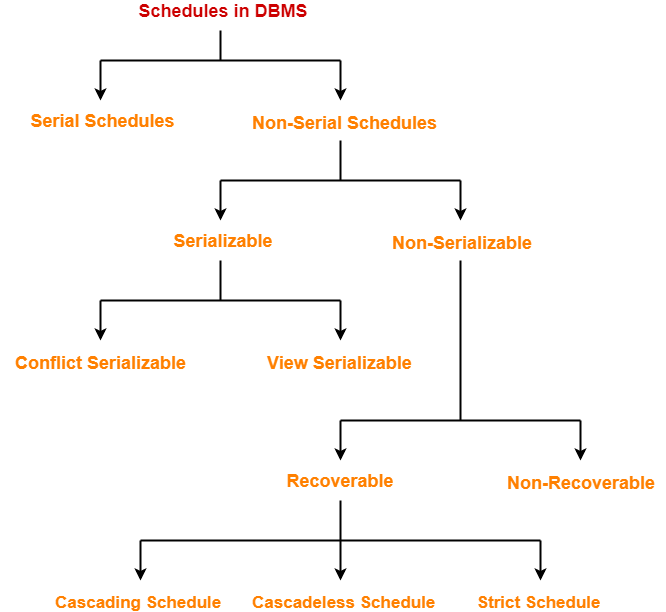
In this article, we will discuss about Serial and Non-Serial Schedules.
Serial Schedules-
In serial schedules,
- All the transactions execute serially one after the other.
- When one transaction executes, no other transaction is allowed to execute.
Characteristics-
Serial schedules are always-
- Consistent
- Recoverable
- Cascadeless
- Strict
Example-01:
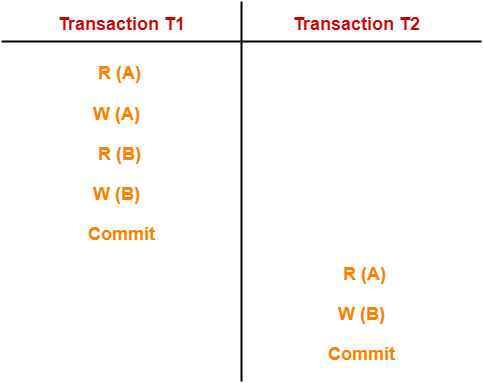
In this schedule,
- There are two transactions T1 and T2 executing serially one after the other.
- Transaction T1 executes first.
- After T1 completes its execution, transaction T2 executes.
- So, this schedule is an example of a Serial Schedule.
Example-02:
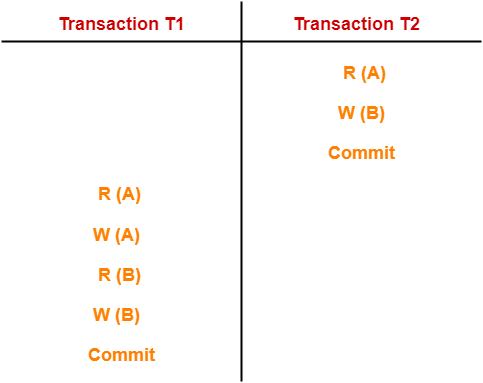
In this schedule,
- There are two transactions T1 and T2 executing serially one after the other.
- Transaction T2 executes first.
- After T2 completes its execution, transaction T1 executes.
- So, this schedule is an example of a Serial Schedule.
Non-Serial Schedules-
In non-serial schedules,
- Multiple transactions execute concurrently.
- Operations of all the transactions are inter leaved or mixed with each other.
Characteristics-
Non-serial schedules are NOT always-
- Consistent
- Recoverable
- Cascadeless
- Strict
Example-01:
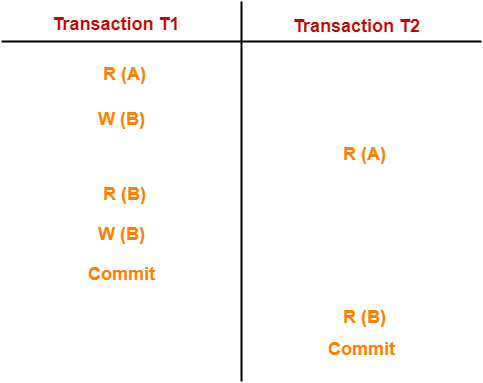
In this schedule,
- There are two transactions T1 and T2 executing concurrently.
- The operations of T1 and T2 are interleaved.
- So, this schedule is an example of a Non-Serial Schedule.
Example-02:
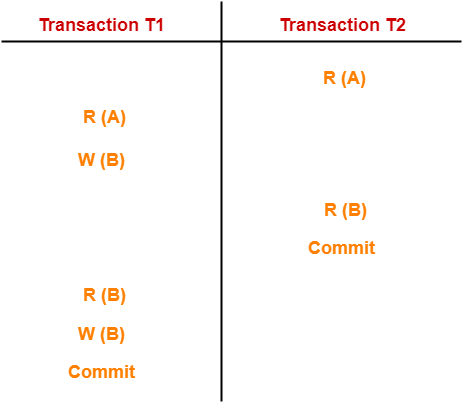
In this schedule,
- There are two transactions T1 and T2 executing concurrently.
- The operations of T1 and T2 are interleaved.
- So, this schedule is an example of a Non-Serial Schedule.
Finding Number Of Schedules-
Consider there are n number of transactions T1, T2, T3 …. , Tn with N1, N2, N3 …. , Nn number of operations respectively.
Total Number of Schedules-
Total number of possible schedules (serial + non-serial) is given by-

Total Number of Serial Schedules-
Total number of serial schedules
= Number of different ways of arranging n transactions
= n!
Total Number of Non-Serial Schedules-
Total number of non-serial schedules
= Total number of schedules – Total number of serial schedules
PRACTICE PROBLEM BASED ON FINDING NUMBER OF SCHEDULES-
Problem-
Consider there are three transactions with 2, 3, 4 operations respectively, find-
- How many total number of schedules are possible?
- How many total number of serial schedules are possible?
- How many total number of non-serial schedules are possible?
Solution-
Total Number of Schedules-
Using the above formula, we have-

Total Number of Serial Schedules-
Total number of serial schedules
= Number of different ways of arranging 3 transactions
= 3!
= 6
Total Number of Non-Serial Schedules-
Total number of non-serial schedules
= Total number of schedules – Total number of serial schedules
= 1260 – 6
= 1254
Next Article- Serializability in DBMS
Get more notes and other study material of Database Management System (DBMS).
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

