Flow Control in Computer Networks-
In computer networks, flow control is defined as-
| A set of procedures which are used for restricting the amount of data that a sender can send to the receiver. |
Flow Control Protocols-
There are various flow control protocols which are classified as-
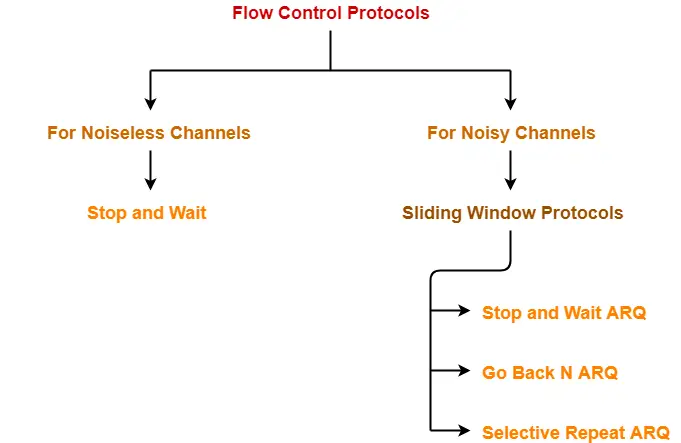
In this article, we will discuss about stop and wait protocol.
Stop and Wait Protocol-
| Stop and Wait Protocol is the simplest flow control protocol. |
It works under the following assumptions-
- Communication channel is perfect.
- No error occurs during transmission.
Working-
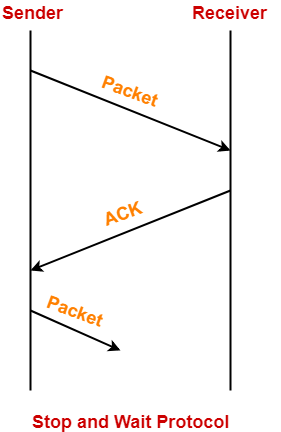
The working of a stop and wait protocol may be explained as-
- Sender sends a data packet to the receiver.
- Sender stops and waits for the acknowledgement for the sent packet from the receiver.
- Receiver receives and processes the data packet.
- Receiver sends an acknowledgement to the sender.
- After receiving the acknowledgement, sender sends the next data packet to the receiver.
These steps are illustrated below-
Analysis-
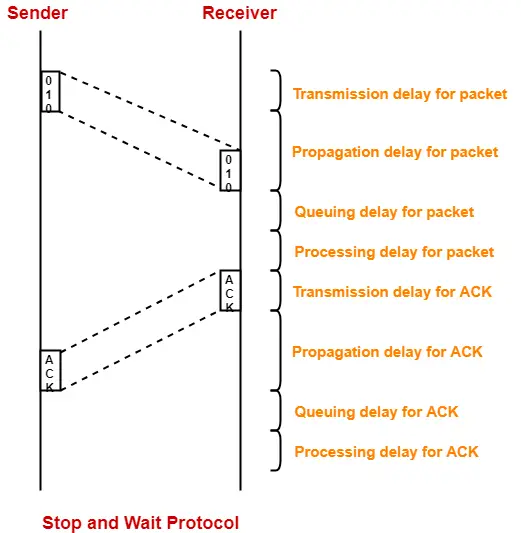
Now, let us analyze in depth how the transmission is actually carried out-
- Sender puts the data packet on the transmission link.
- Data packet propagates towards the receiver’s end.
- Data packet reaches the receiver and waits in its buffer.
- Receiver processes the data packet.
- Receiver puts the acknowledgement on the transmission link.
- Acknowledgement propagates towards the sender’s end.
- Acknowledgement reaches the sender and waits in its buffer.
- Sender processes the acknowledgement.
These steps are illustrated below-
Also Read- Delays in Computer Networks
Total Time-
| Total time taken in sending one data packet
= (Transmission delay + Propagation delay + Queuing delay + Processing delay)packet + (Transmission delay + Propagation delay + Queuing delay + Processing delay)ACK |
Assume-
- Queuing delay and processing delay to be zero at both sender and receiver side.
- Transmission time for the acknowledgement to be zero since it’s size is very small.
Under the above assumptions.
| Total time taken in sending one data packet
= (Transmission delay + Propagation delay)packet + (Propagation delay)ACK |
We know,
- Propagation delay depends on the distance and speed.
- So, it would be same for both data packet and acknowledgement.
So, we have-
| Total time taken in sending one data packet
= (Transmission delay)packet + 2 x Propagation delay |
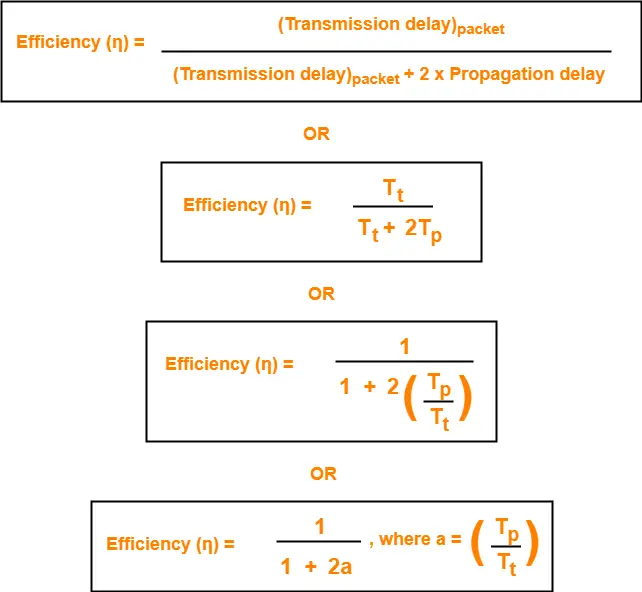
Efficiency-
Efficiency of any flow control control protocol is given by-
| Efficiency (η) = Useful Time / Total Time |
where-
- Useful time = Transmission delay of data packet = (Transmission delay)packet
- Useless time = Time for which sender is forced to wait and do nothing = 2 x Propagation delay
- Total time = Useful time + Useless time
Thus,
Factors Affecting Efficiency-
We know,
Efficiency (η)
= (Transmission delay)packet / { (Transmission delay)packet + 2 x Propagation delay }
Dividing numerator and denominator by (Transmission delay)packet, we get-
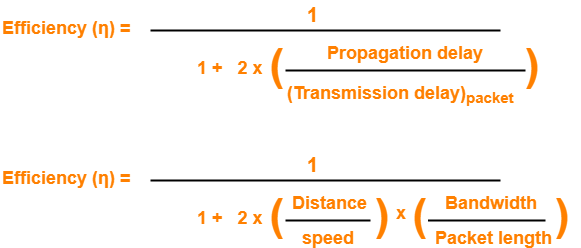
From here, we can observe-
- Efficiency (η) ∝ 1 / Distance between sender and receiver
- Efficiency (η) ∝ 1 / Bandwidth
- Efficiency (η) ∝ Transmission speed
- Efficiency (η) ∝ Length of data packet
Throughput-
- Number of bits that can be sent through the channel per second is called as its throughput.

Round Trip Time-
| Round Trip Time = 2 x Propagation delay |
Advantages-
The advantages of stop and wait protocol are-
- It is very simple to implement.
- The incoming packet from receiver is always an acknowledgement.
Limitations-
The limitations of stop and wait protocol are-
Point-01:
It is extremely inefficient because-
- It makes the transmission process extremely slow.
- It does not use the bandwidth entirely as each single packet and acknowledgement uses the entire time to traverse the link.
Point-02:
If the data packet sent by the sender gets lost, then-
- Sender will keep waiting for the acknowledgement for infinite time.
- Receiver will keep waiting for the data packet for infinite time.
Point-03:
If acknowledgement sent by the receiver gets lost, then-
- Sender will keep waiting for the acknowledgement for infinite time.
- Receiver will keep waiting for another data packet for infinite time.
Important Notes-
Note-01:
Efficiency may also be referred by the following names-
- Line Utilization
- Link Utilization
- Sender Utilization
- Utilization of Sender
Note-02:
Throughput may also be referred by the following names-
- Bandwidth Utilization
- Effective Bandwidth
- Maximum data rate possible
- Maximum achievable throughput
Note-03:
Stop and Wait protocol performs better for LANs than WANs.
This is because-
- Efficiency of the protocol is inversely proportional to the distance between sender and receiver.
- So, the protocol performs better where the distance between sender and receiver is less.
- The distance is less in LANs as compared to WANs.
To gain better understanding about Stop and Wait Protocol,
Next Article- Stop and Wait ARQ
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.


