Construction Of DFA-
In this article, we will learn the construction of DFA.
Type-01 Problems-
In Type-01 problems, we will discuss the construction of DFA for languages consisting of strings ending with a particular substring.
Steps To Construct DFA-
Following steps are followed to construct a DFA for Type-01 problems-
Step-01:
- Determine the minimum number of states required in the DFA.
- Draw those states.
Use the following rule to determine the minimum number of states-
RULECalculate the length of substring. All strings ending with ‘n’ length substring will always require minimum (n+1) states in the DFA. |
Step-02:
- Decide the strings for which DFA will be constructed.
- The method for deciding the strings has been discussed in this Video.
Step-03:
- Construct a DFA for the strings decided in Step-02.
Remember the following rule while constructing the DFA-
RULEWhile constructing a DFA,
|
Step-04:
- Send all the left possible combinations to the starting state.
- Do not send the left possible combinations over the dead state.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON CONSTRUCTION OF DFA-
Problem-01:
Draw a DFA for the language accepting strings ending with ’01’ over input alphabets ∑ = {0, 1}
Solution-
Regular expression for the given language = (0 + 1)*01
Step-01:
- All strings of the language ends with substring “01”.
- So, length of substring = 2.
Thus, Minimum number of states required in the DFA = 2 + 1 = 3.
It suggests that minimized DFA will have 3 states.
Step-02:
We will construct DFA for the following strings-
- 01
- 001
- 0101
Step-03:
The required DFA is-

Problem-02:
Draw a DFA for the language accepting strings ending with ‘abb’ over input alphabets ∑ = {a, b}
Solution-
Regular expression for the given language = (a + b)*abb
Step-01:
- All strings of the language ends with substring “abb”.
- So, length of substring = 3.
Thus, Minimum number of states required in the DFA = 3 + 1 = 4.
It suggests that minimized DFA will have 4 states.
Step-02:
We will construct DFA for the following strings-
- abb
- aabb
- ababb
- abbabb
Step-03:
The required DFA is-

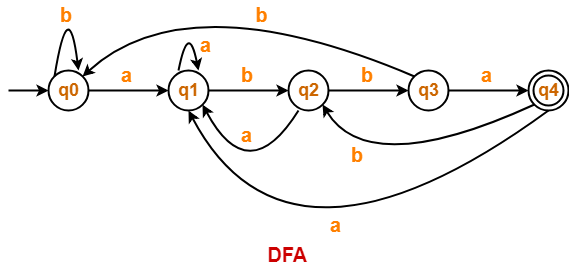
Problem-03:
Draw a DFA for the language accepting strings ending with ‘abba’ over input alphabets ∑ = {a, b}
Solution-
Regular expression for the given language = (a + b)*abba
Step-01:
- All strings of the language ends with substring “abba”.
- So, length of substring = 4.
Thus, Minimum number of states required in the DFA = 4 + 1 = 5.
It suggests that minimized DFA will have 5 states.
Step-02:
We will construct DFA for the following strings-
- abba
- aabba
- ababba
- abbabba
- abbaabba
Step-03:
The required DFA is-
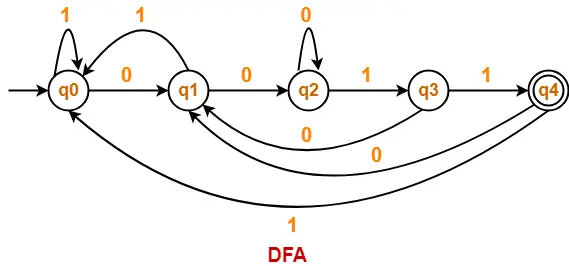
Problem-04:
Draw a DFA for the language accepting strings ending with ‘0011’ over input alphabets ∑ = {0, 1}
Solution-
Regular expression for the given language = (0 + 1)*0011
Step-01:
- All strings of the language ends with substring “0011”.
- So, length of substring = 4.
Thus, Minimum number of states required in the DFA = 4 + 1 = 5.
It suggests that minimized DFA will have 5 states.
Step-02:
We will construct DFA for the following strings-
- 0011
- 00011
- 000011
- 0010011
- 00110011
Step-03:
The required DFA is-
Also Read- Converting DFA to Regular Expression
To gain better understanding about Construction of DFA,
Download Handwritten Notes Here-
Next Article- Construction of DFA | Type-02 Problems
Get more notes and other study material of Theory of Automata and Computation.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.